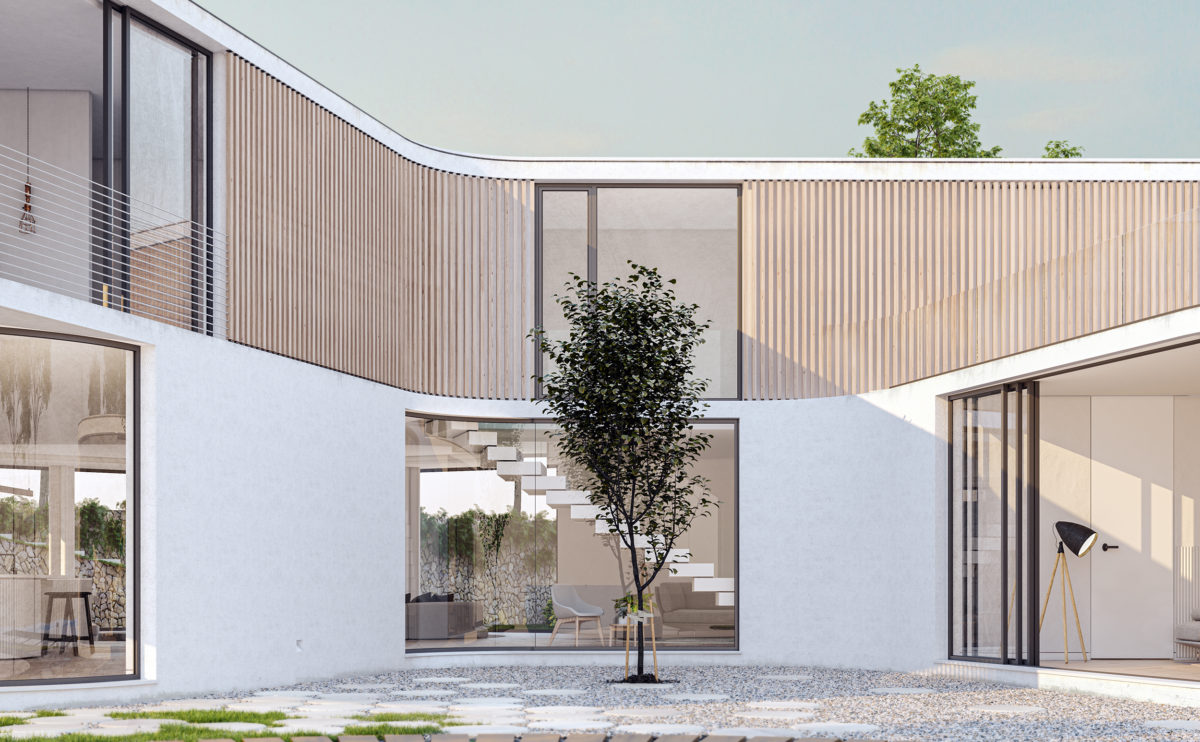
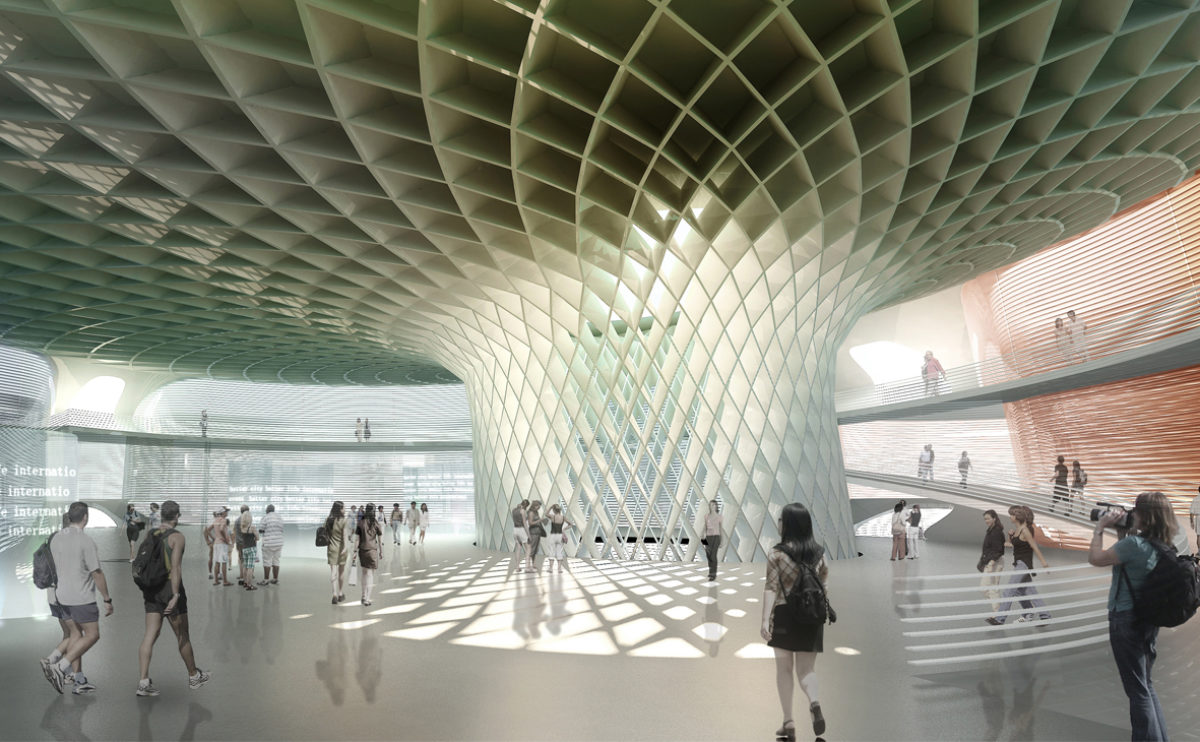
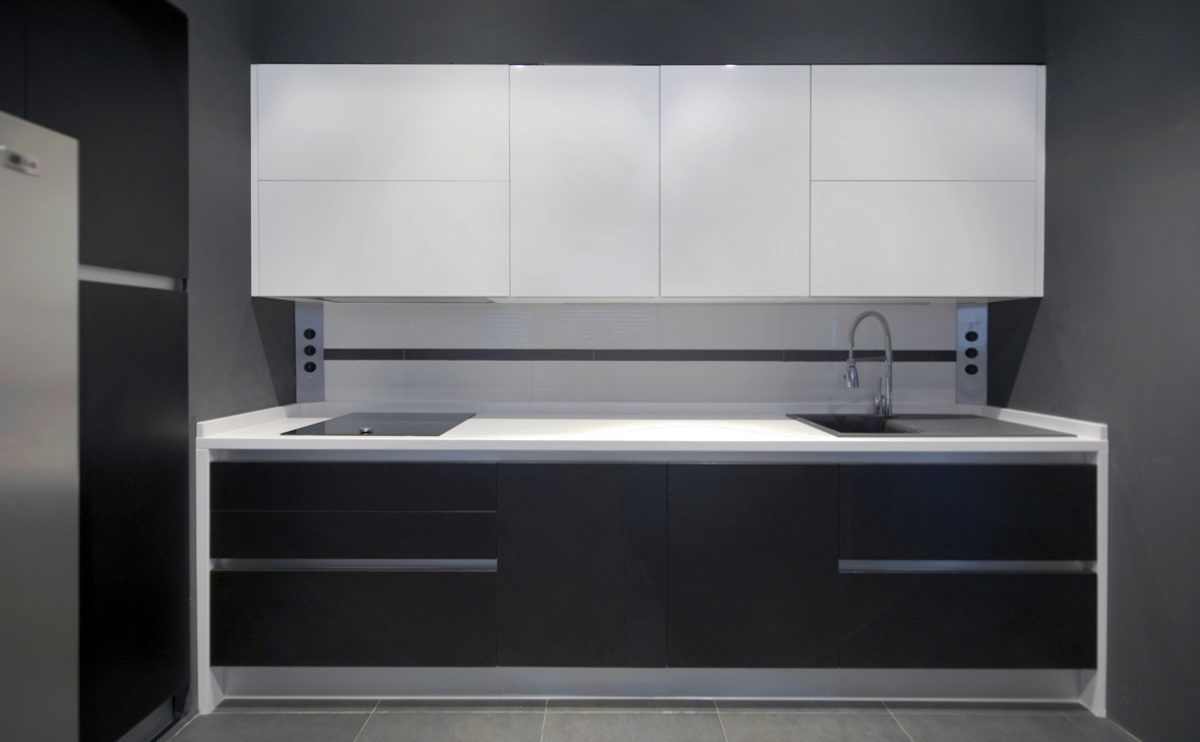
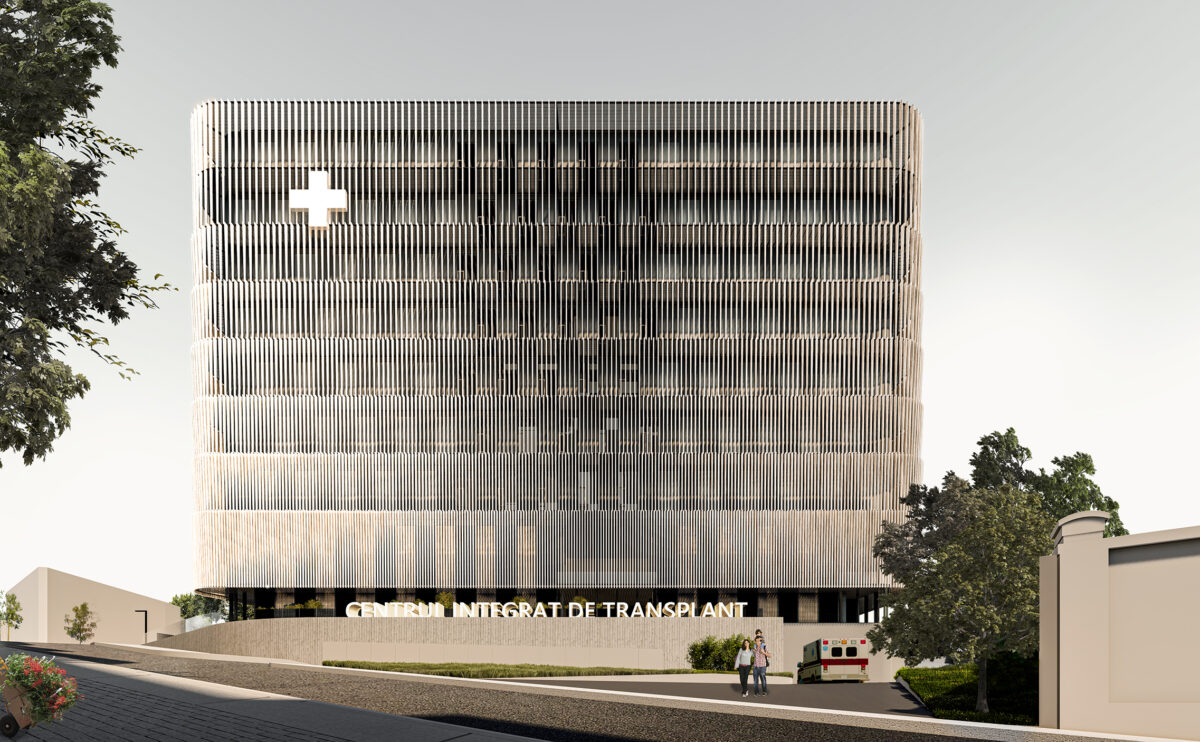
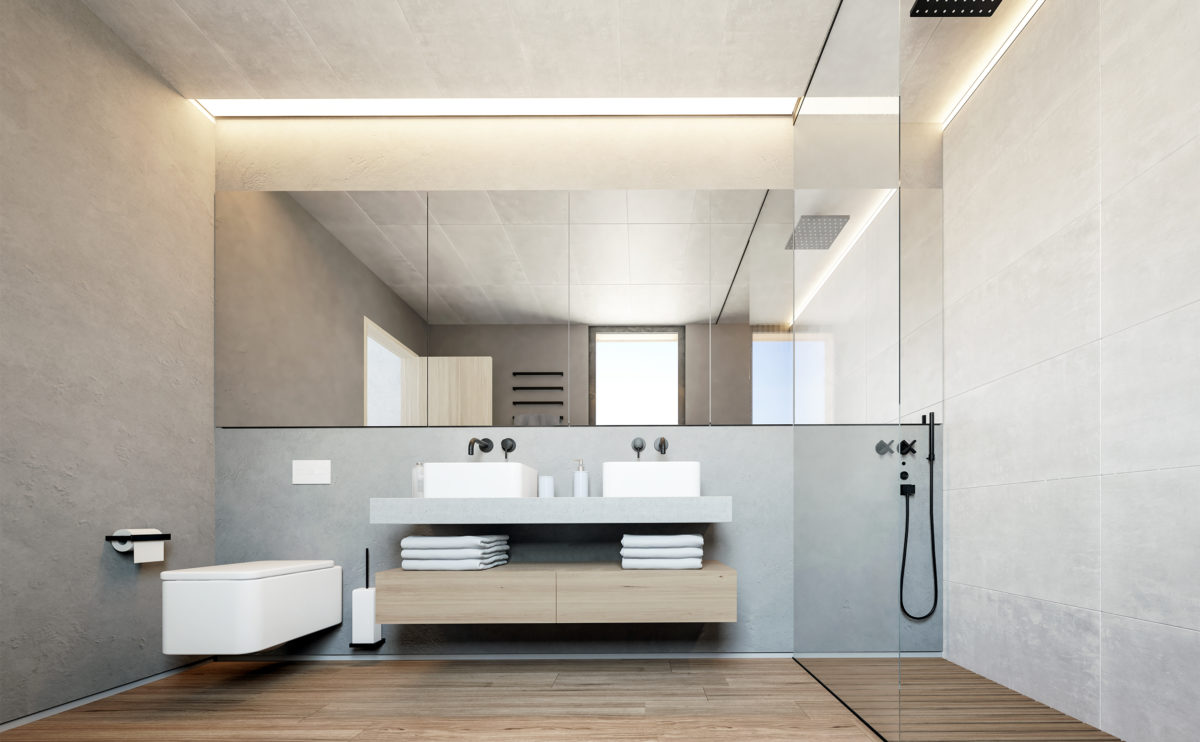
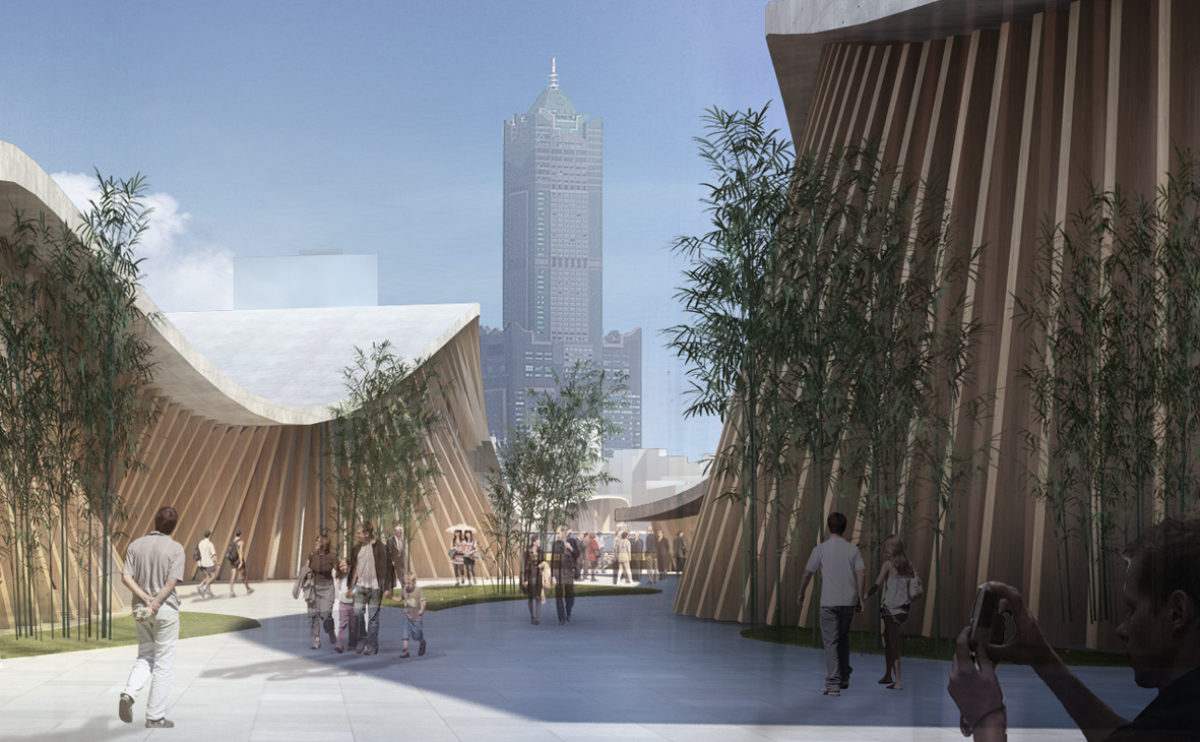
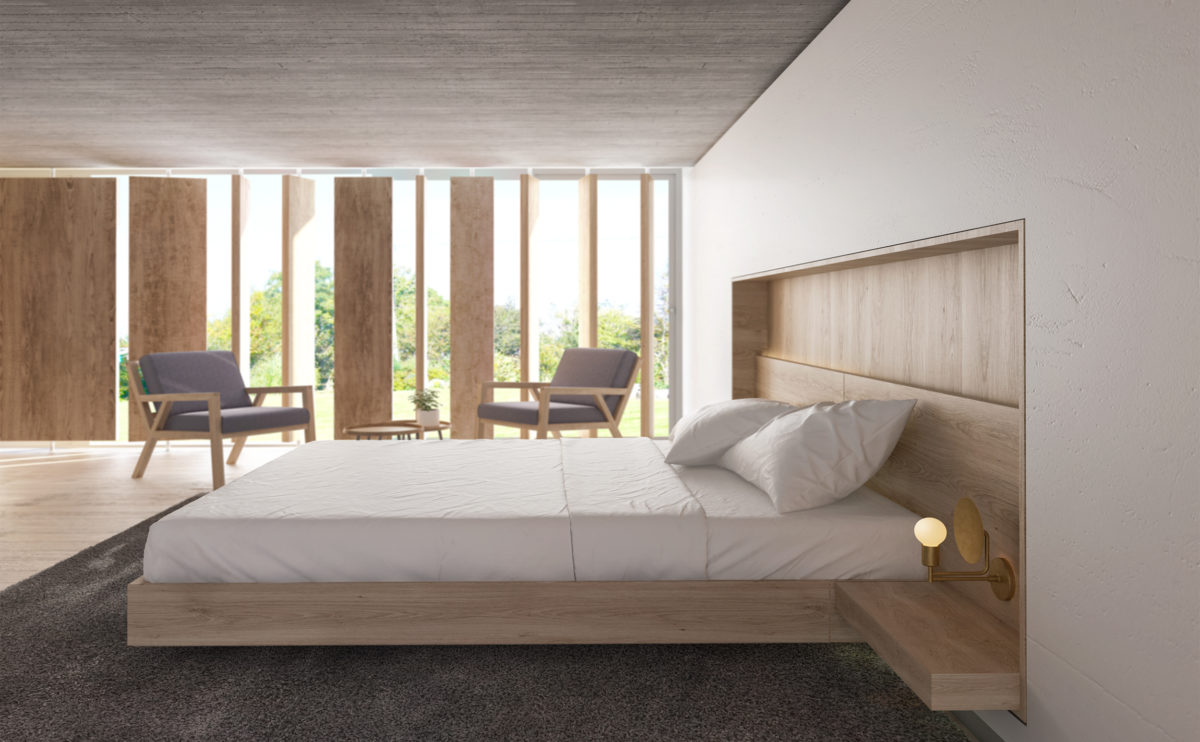
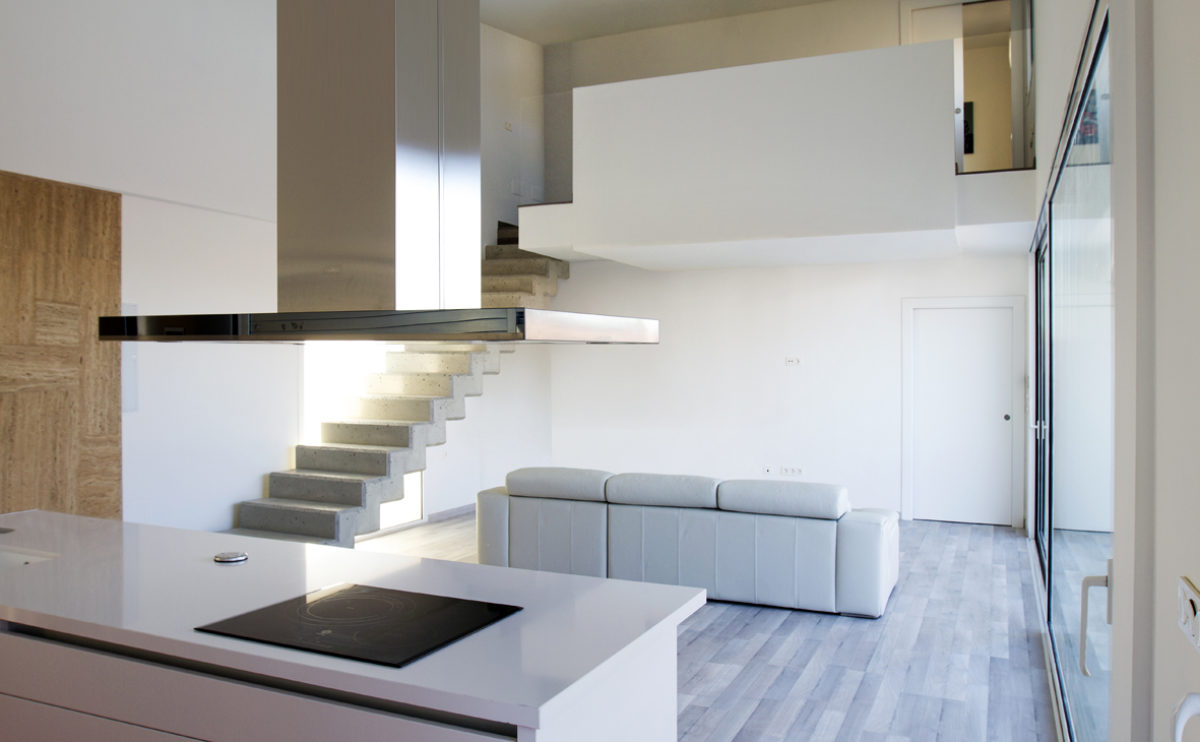
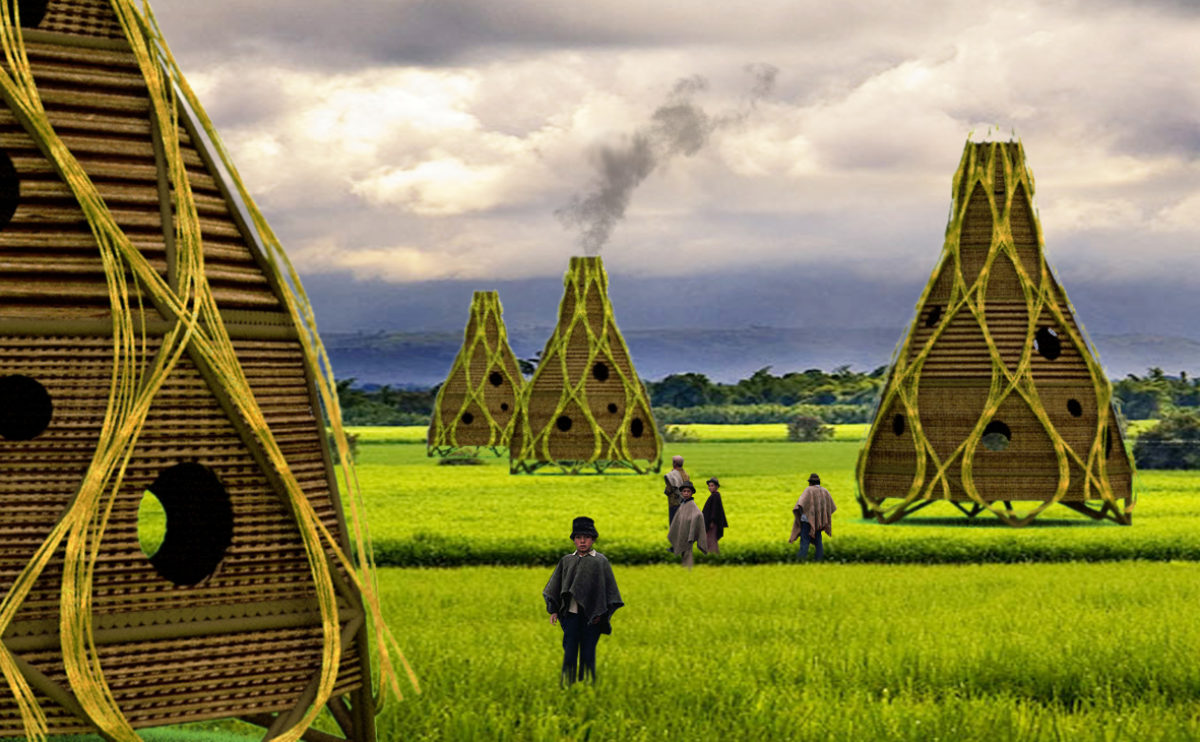
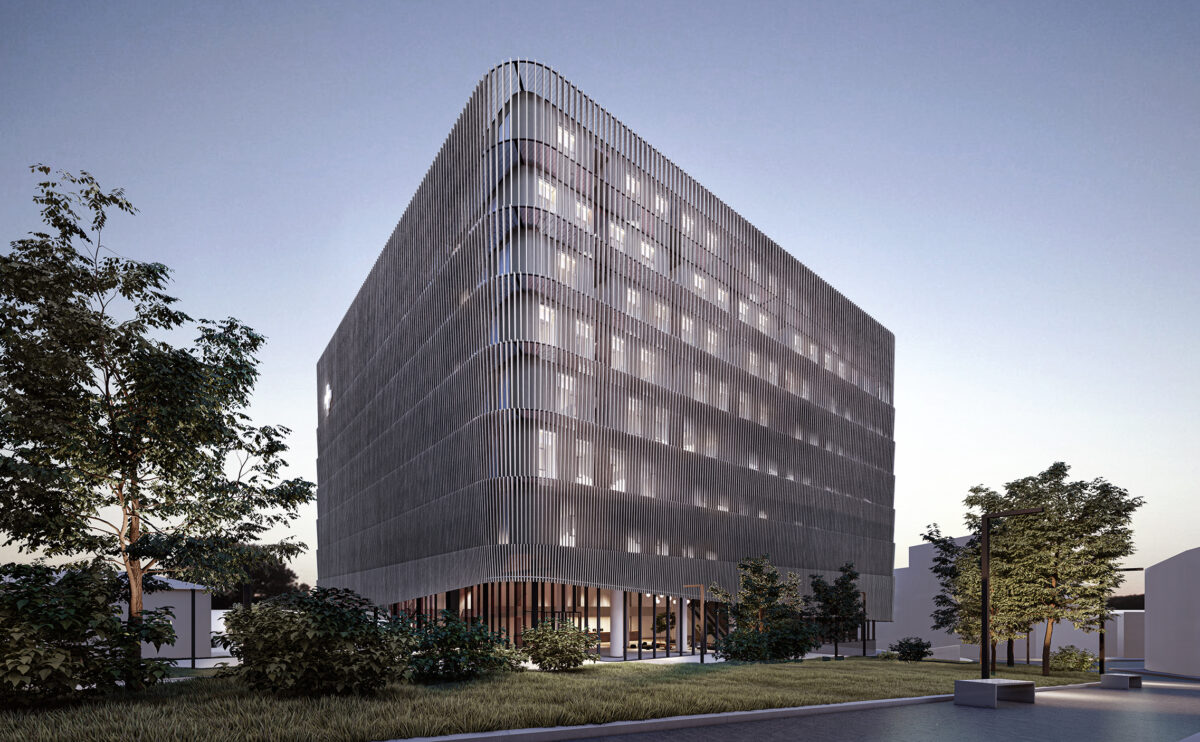
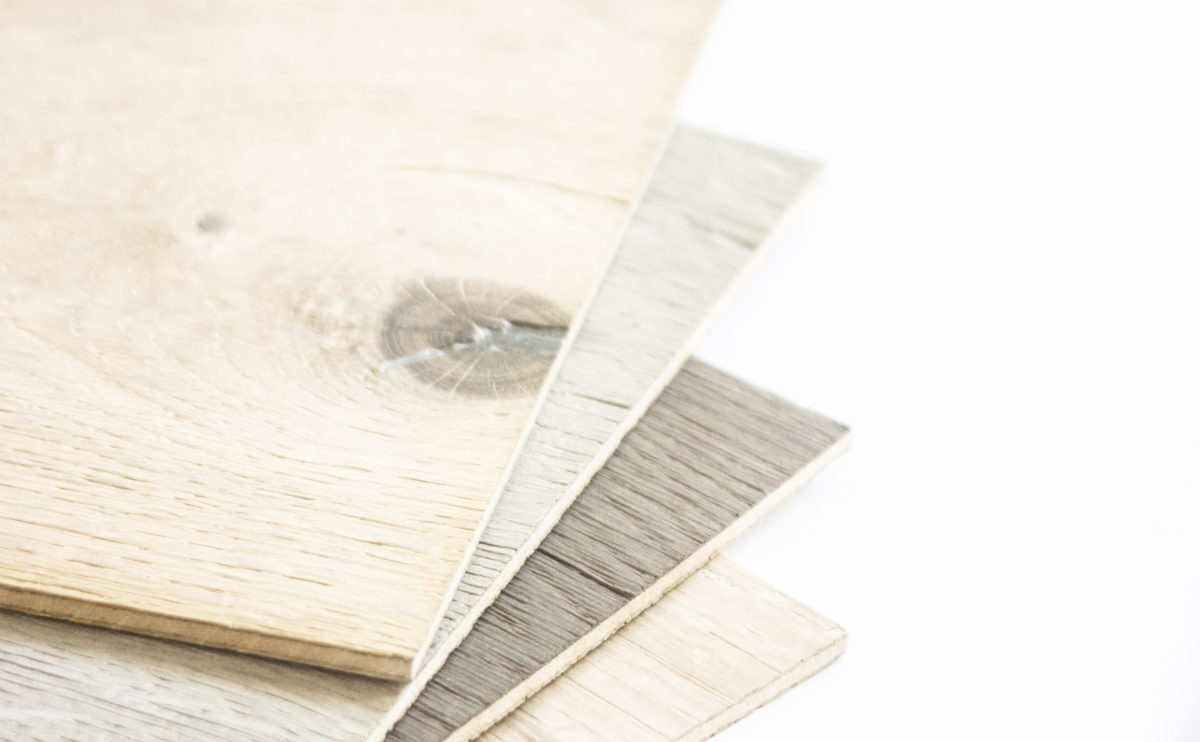
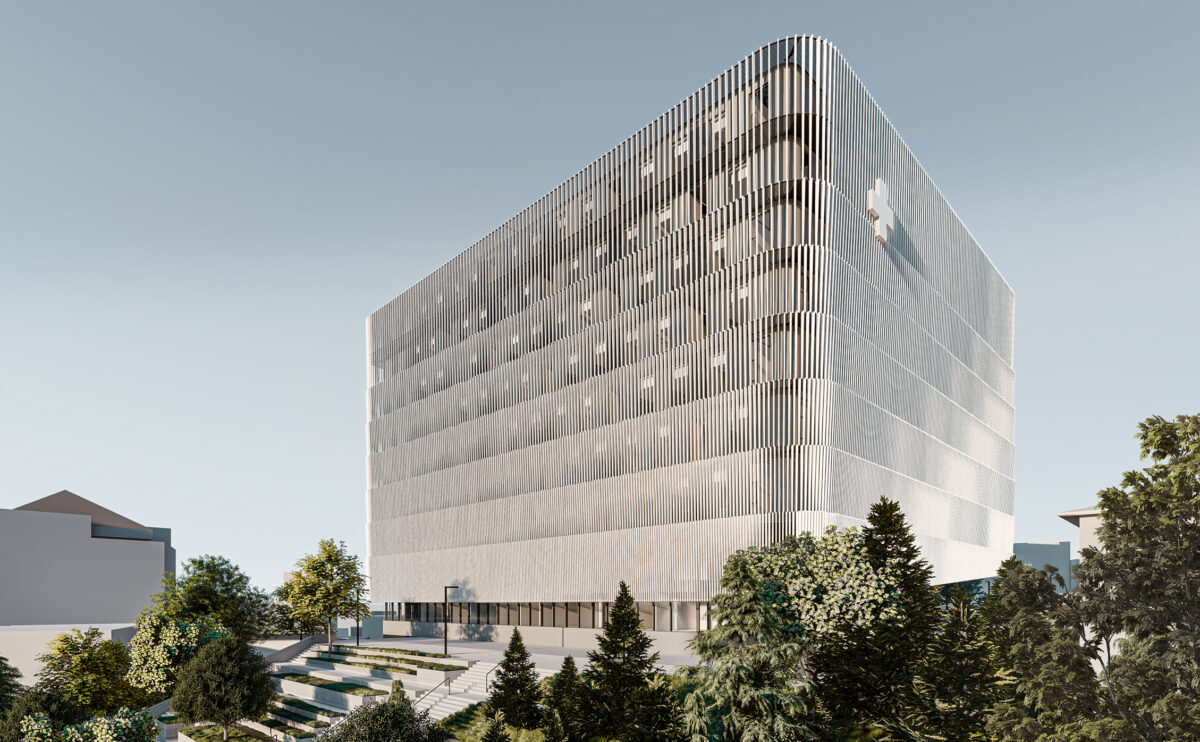
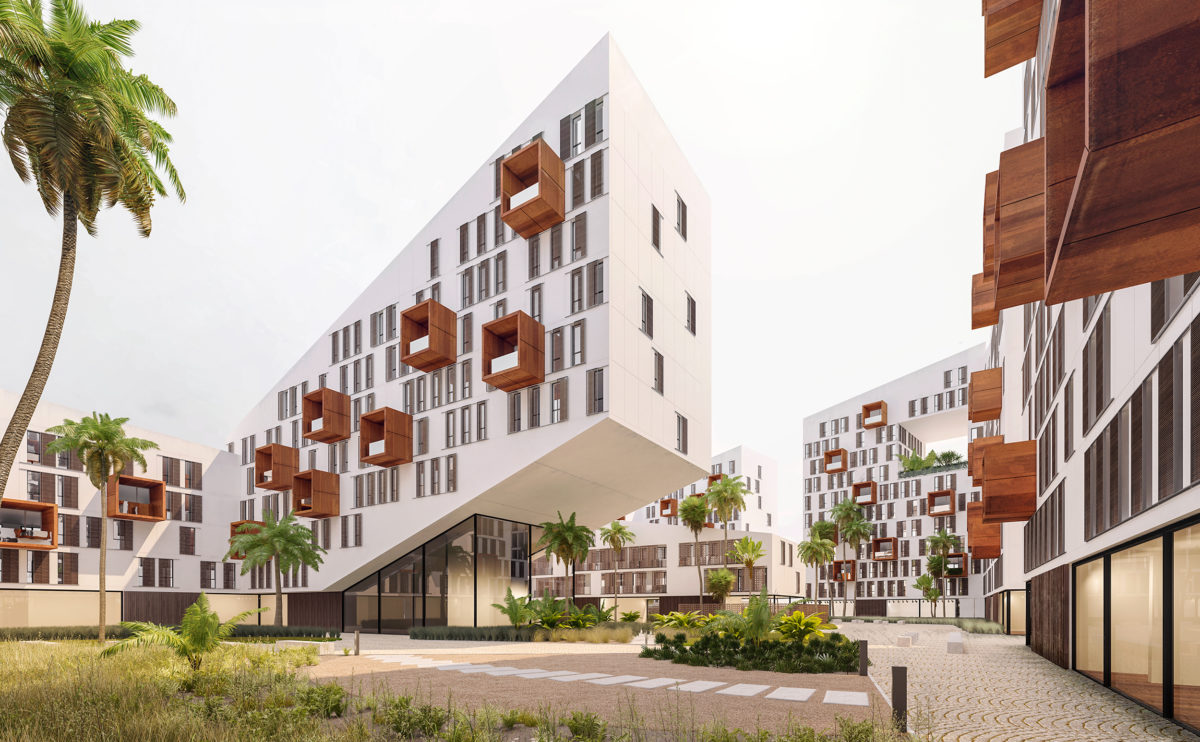
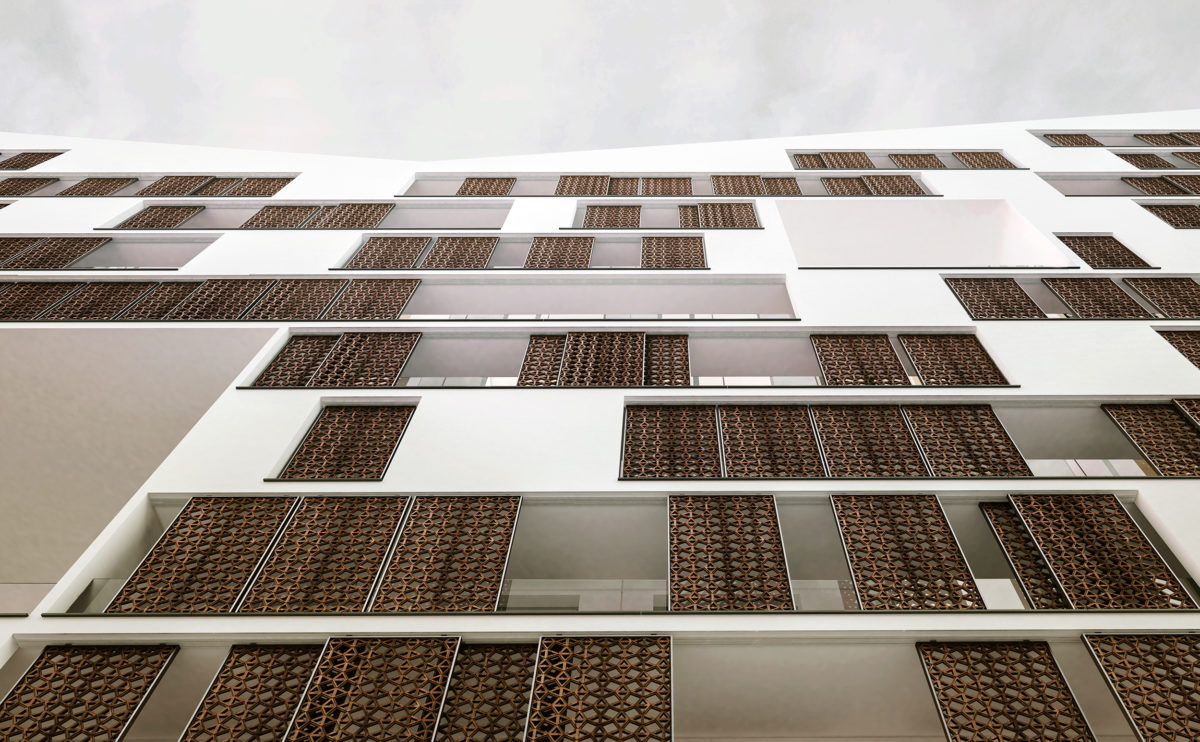
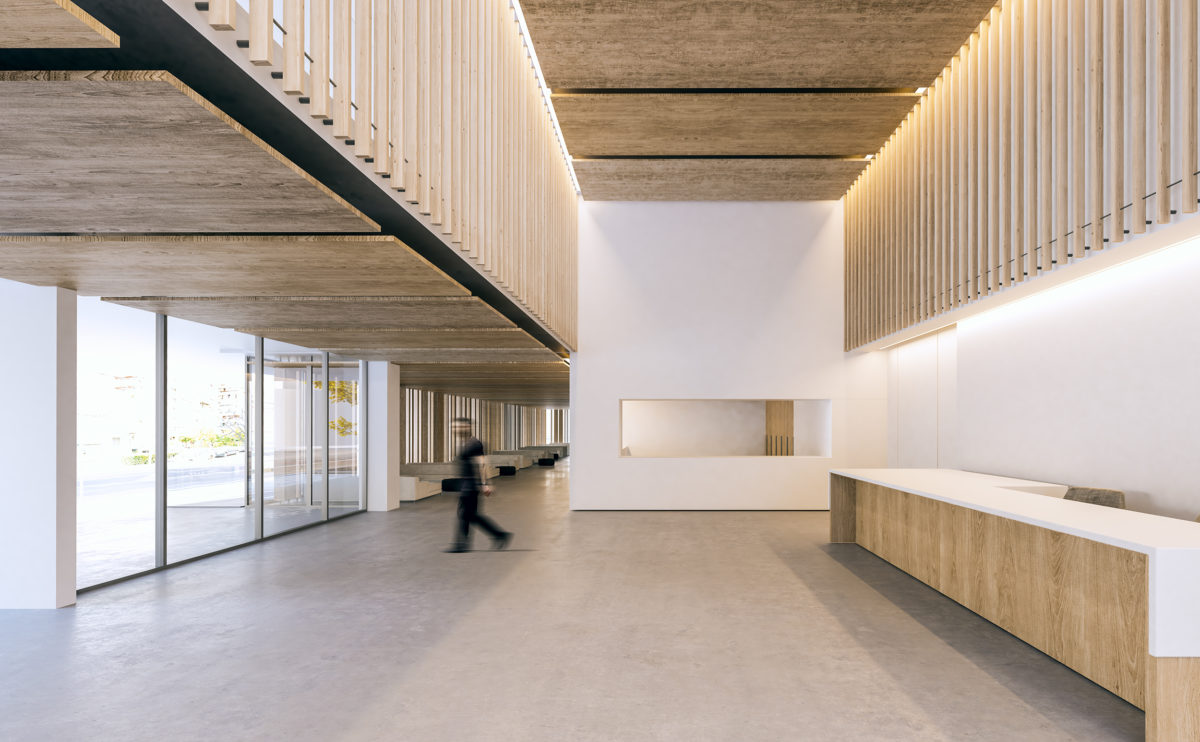
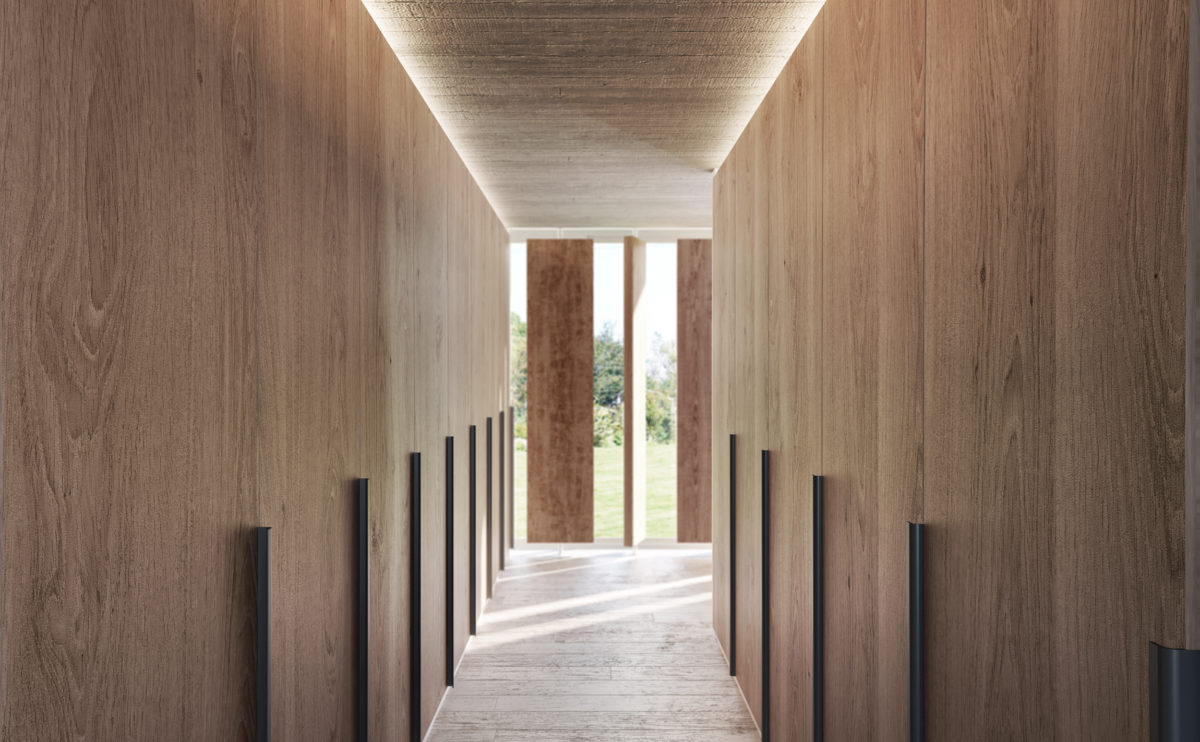
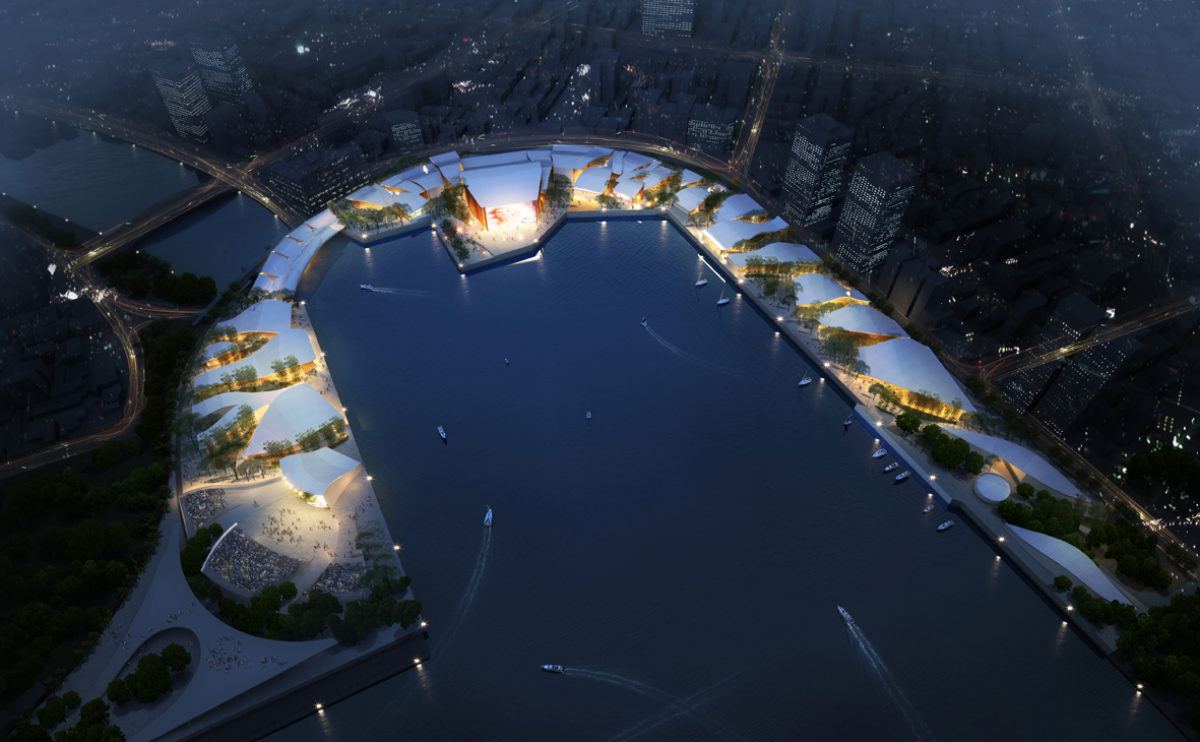
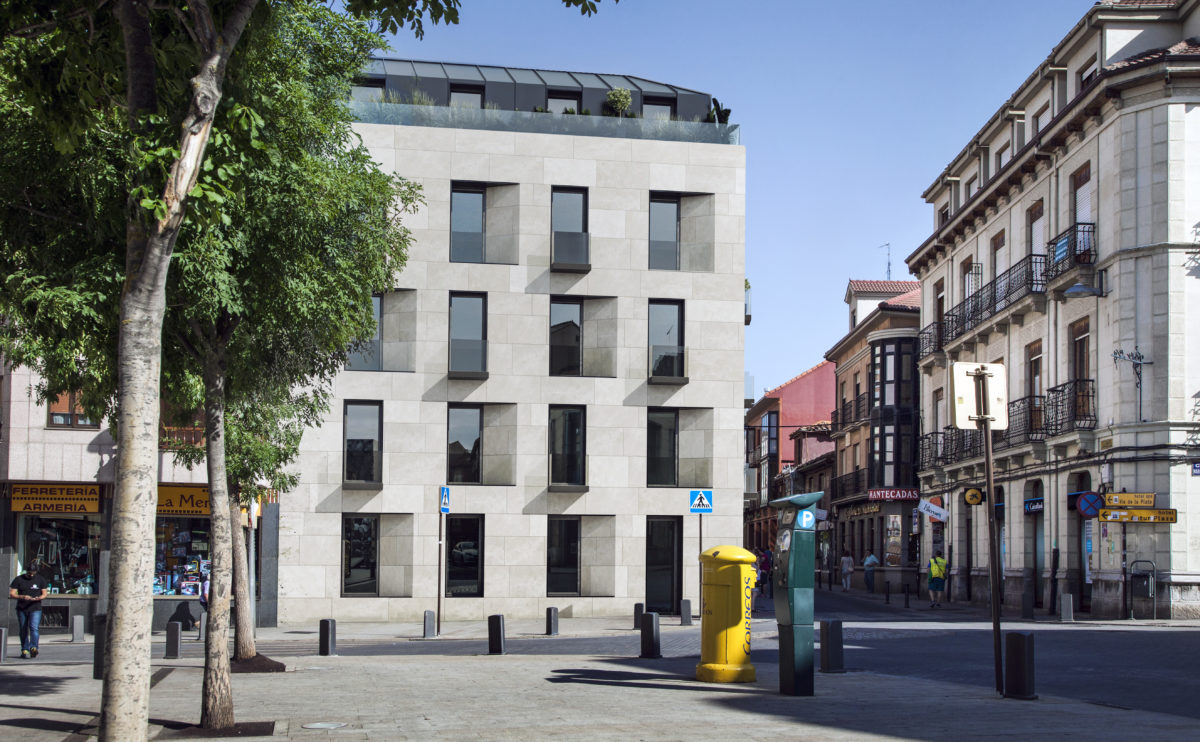
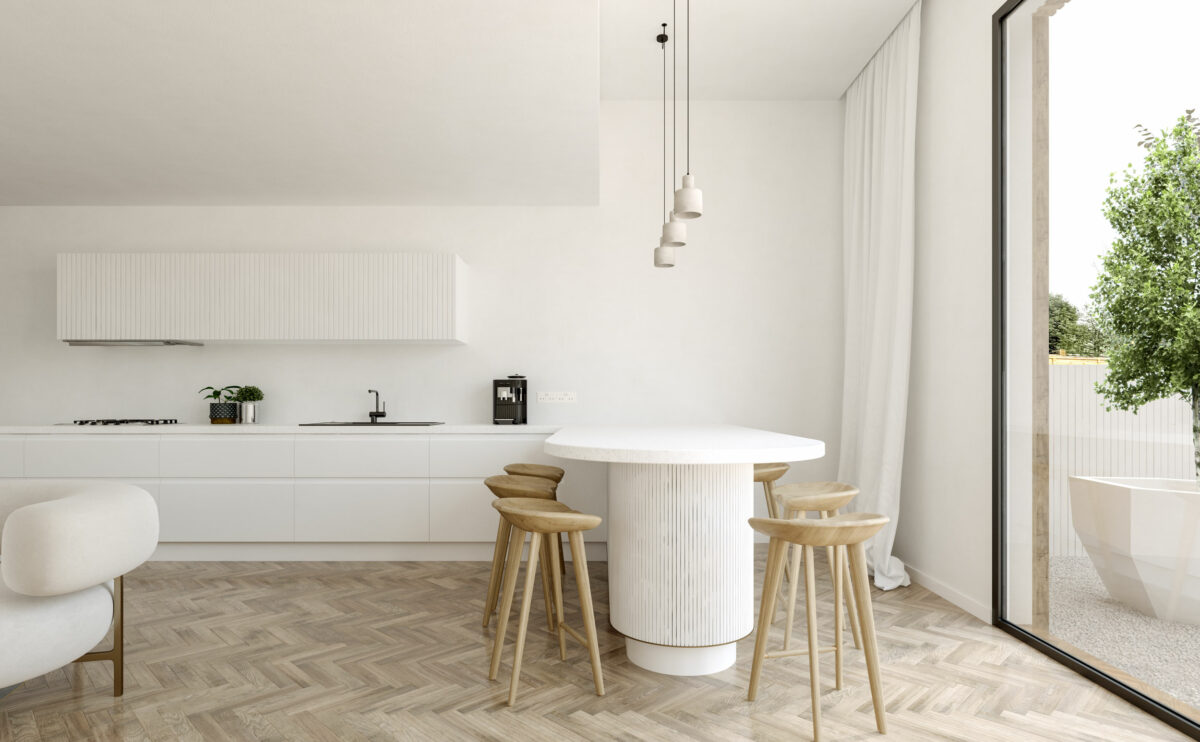
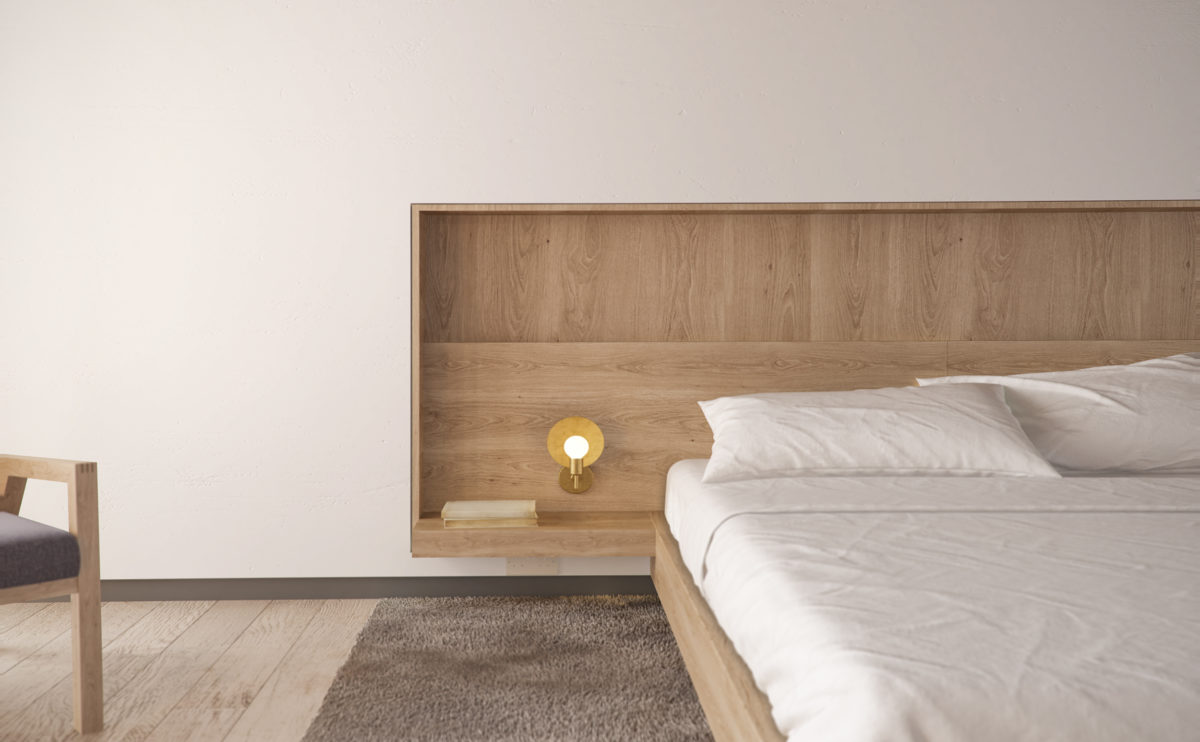
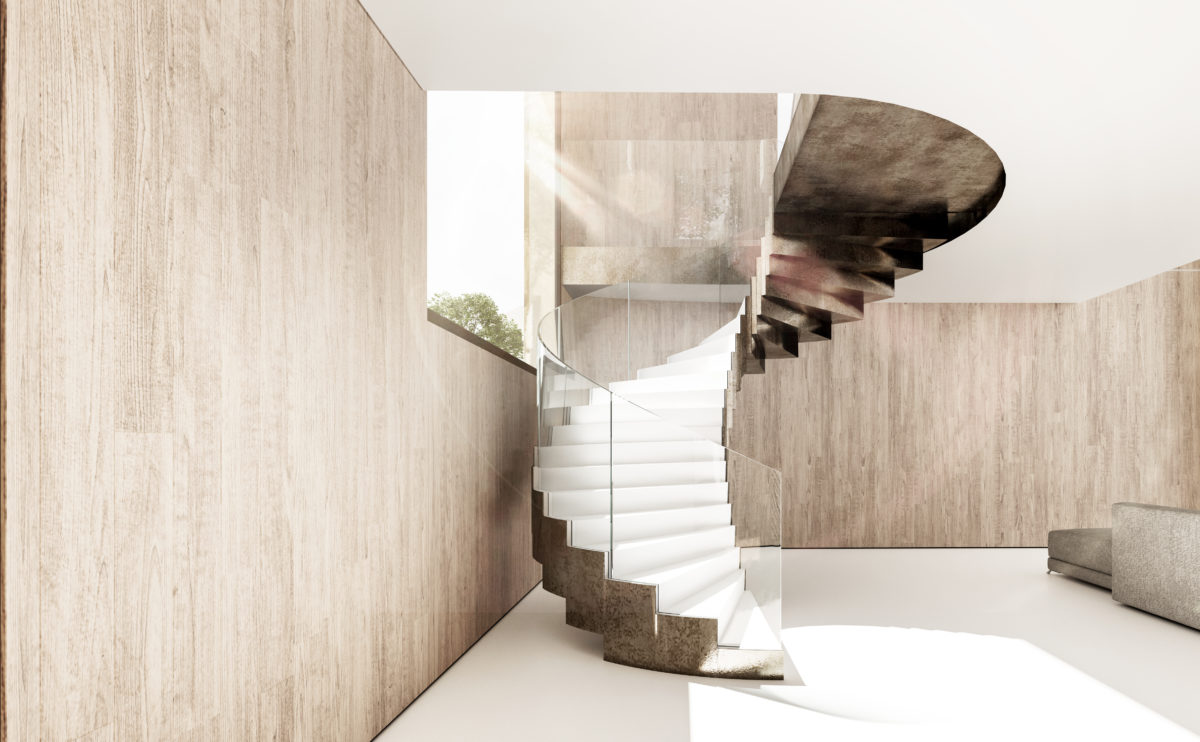
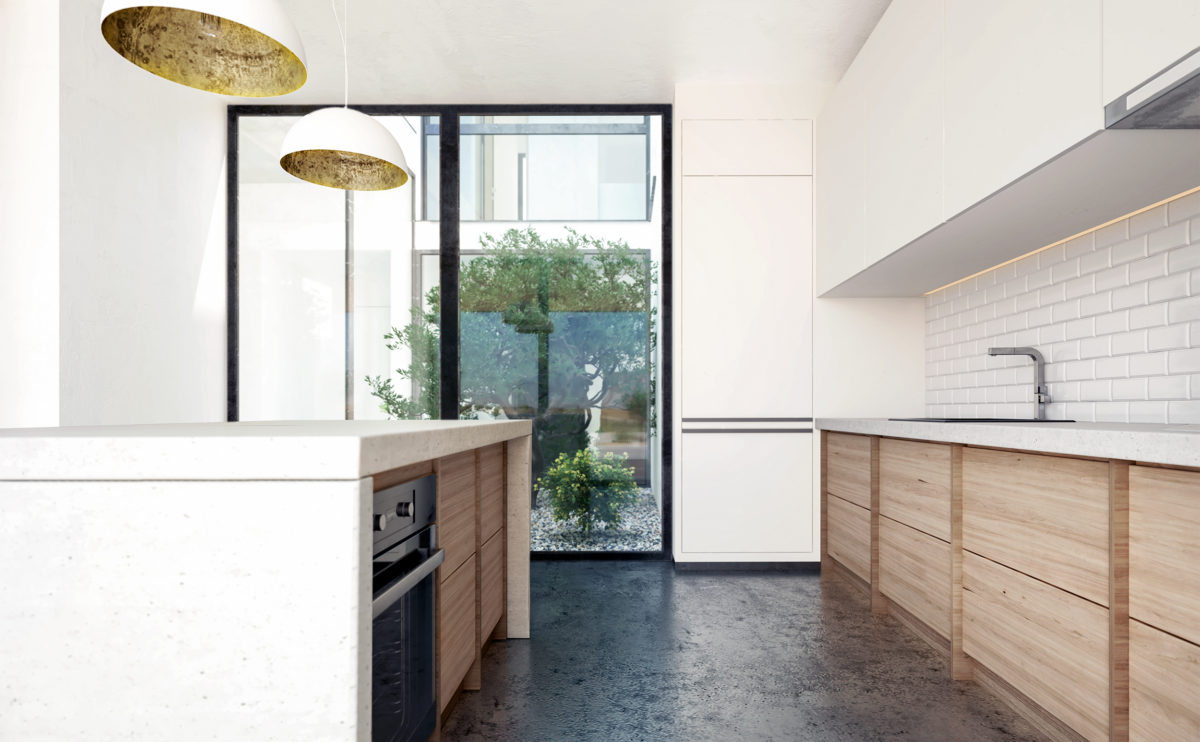
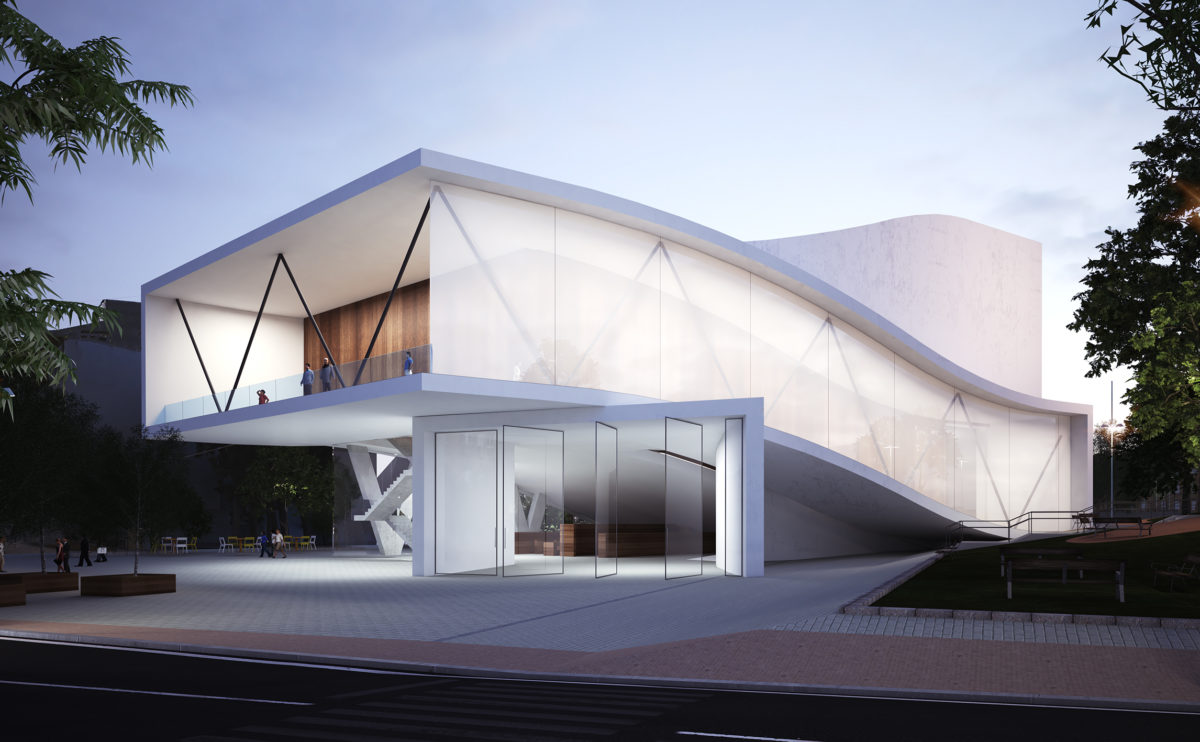
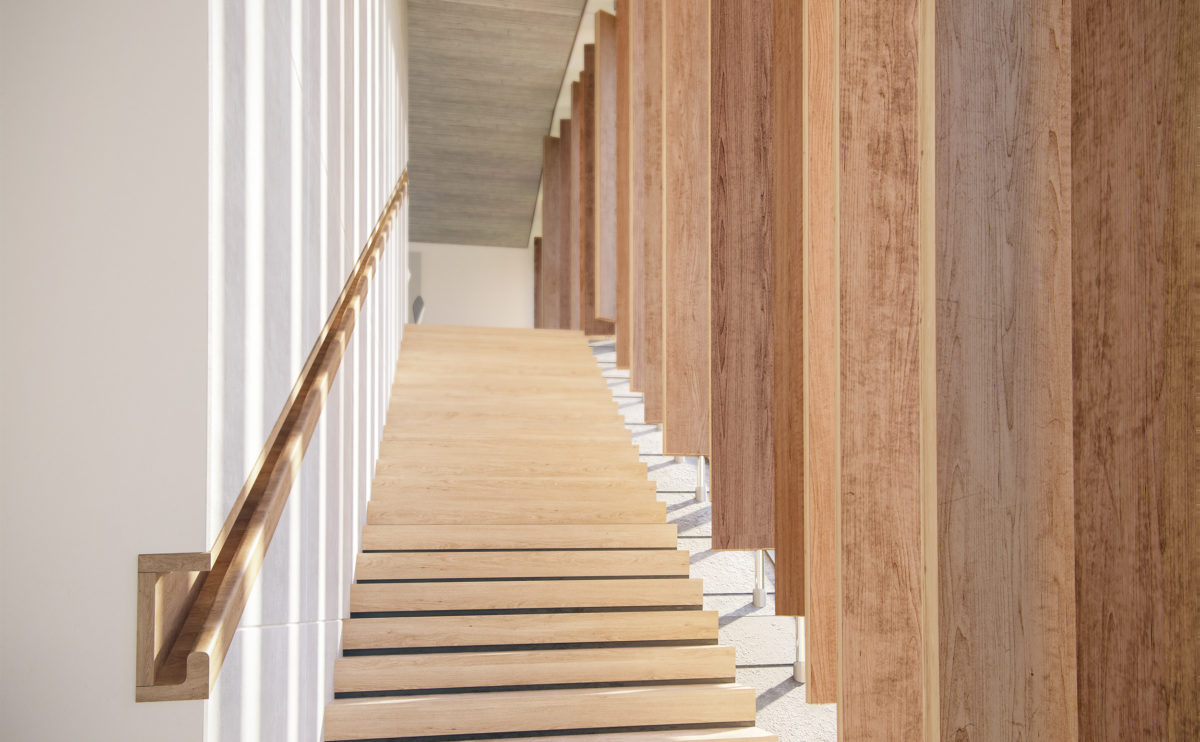
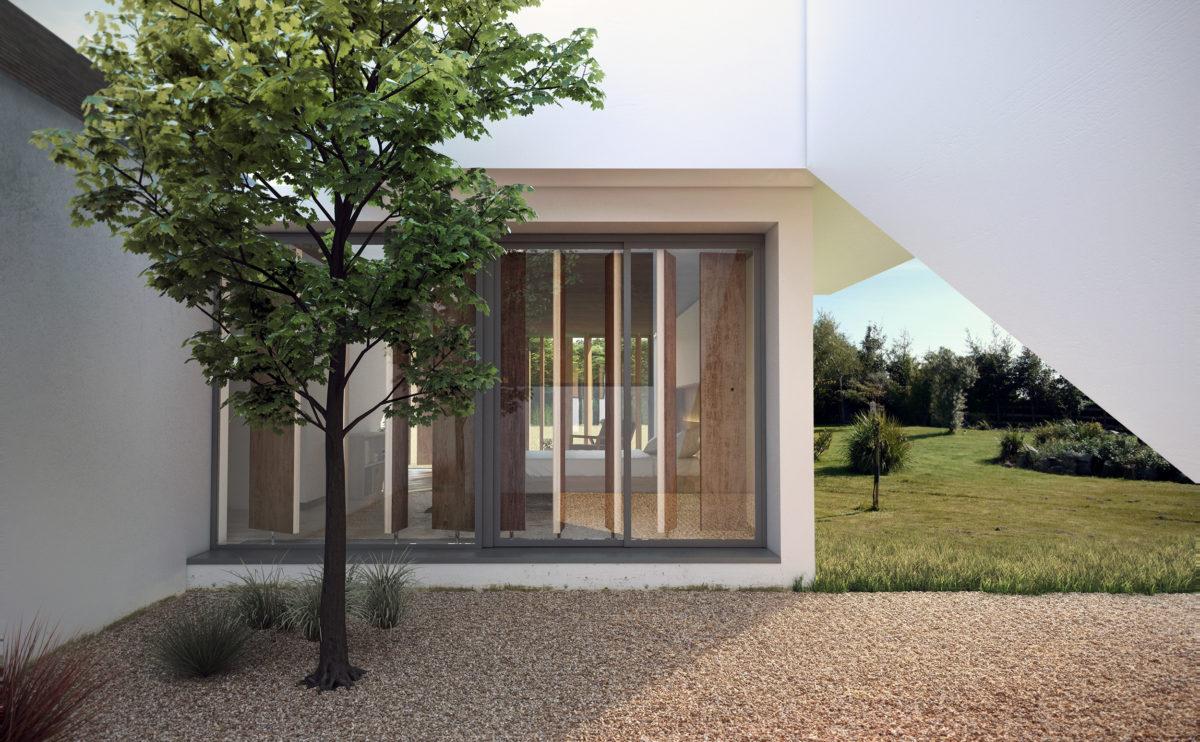
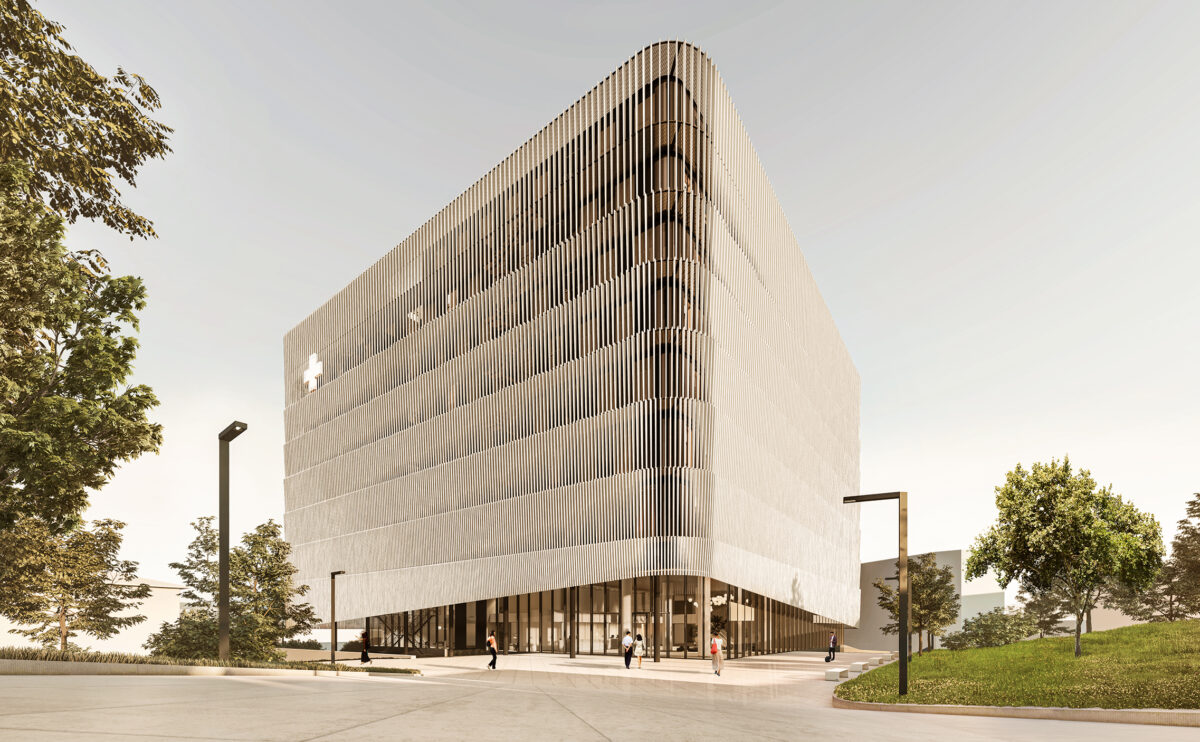
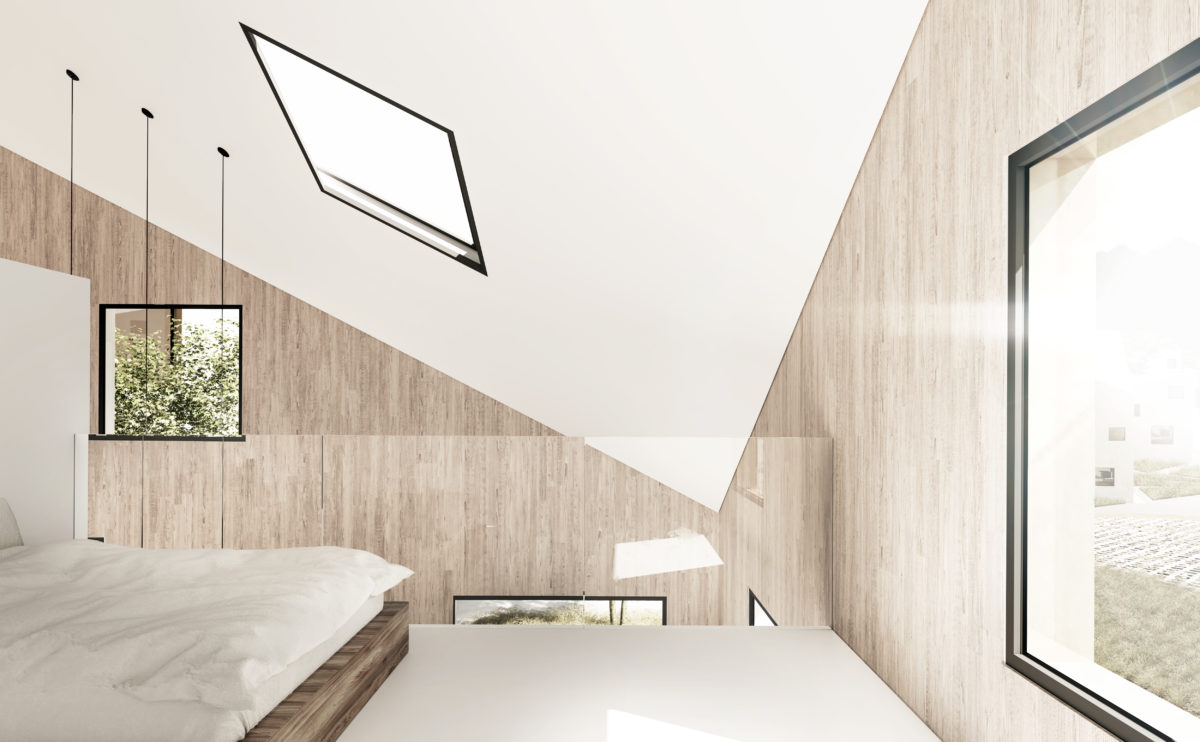
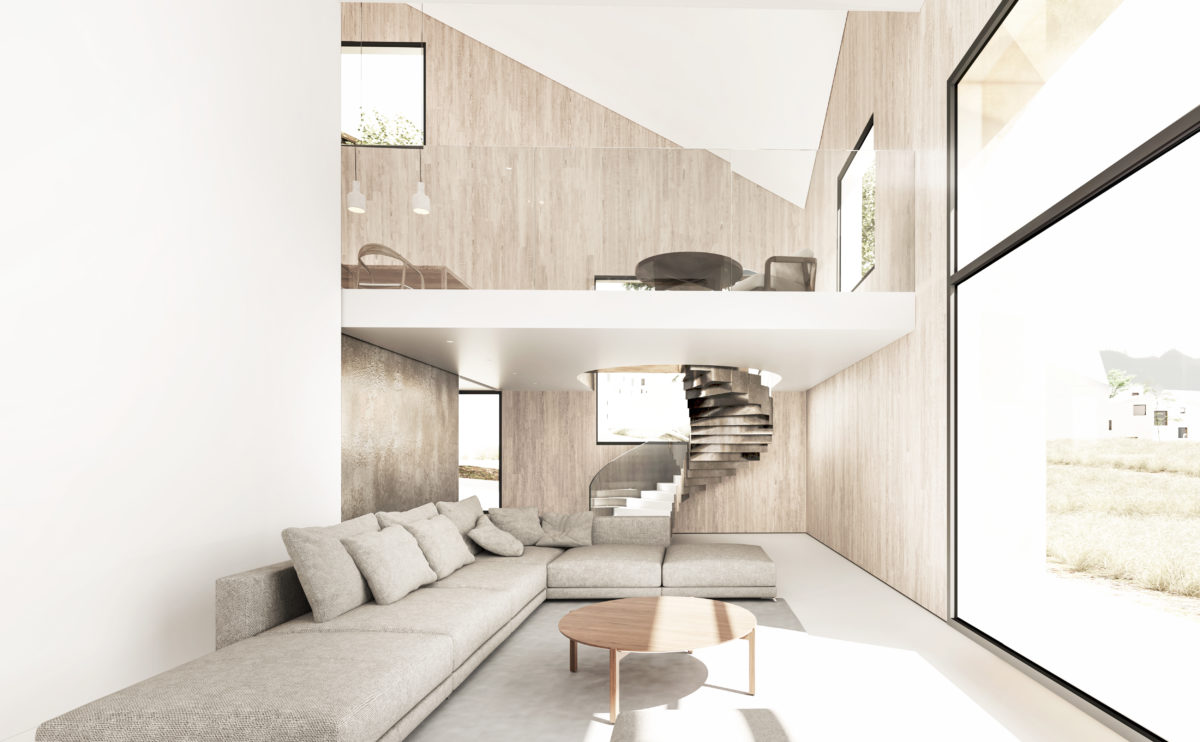
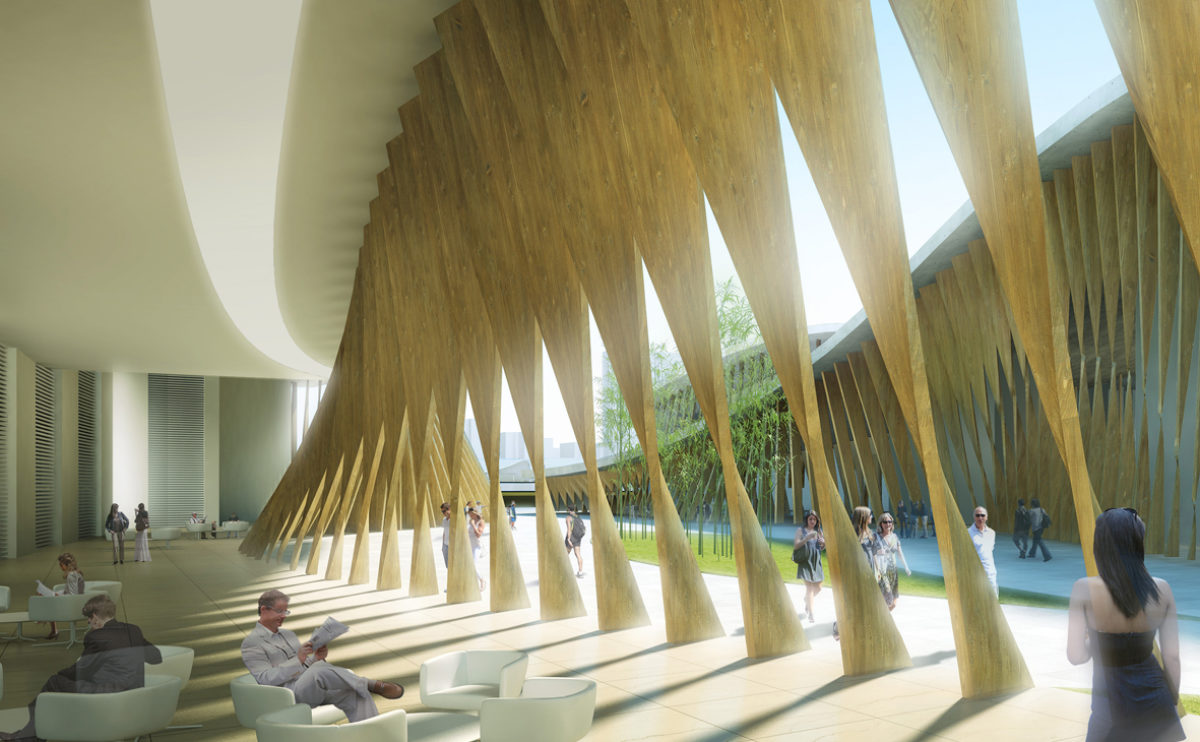
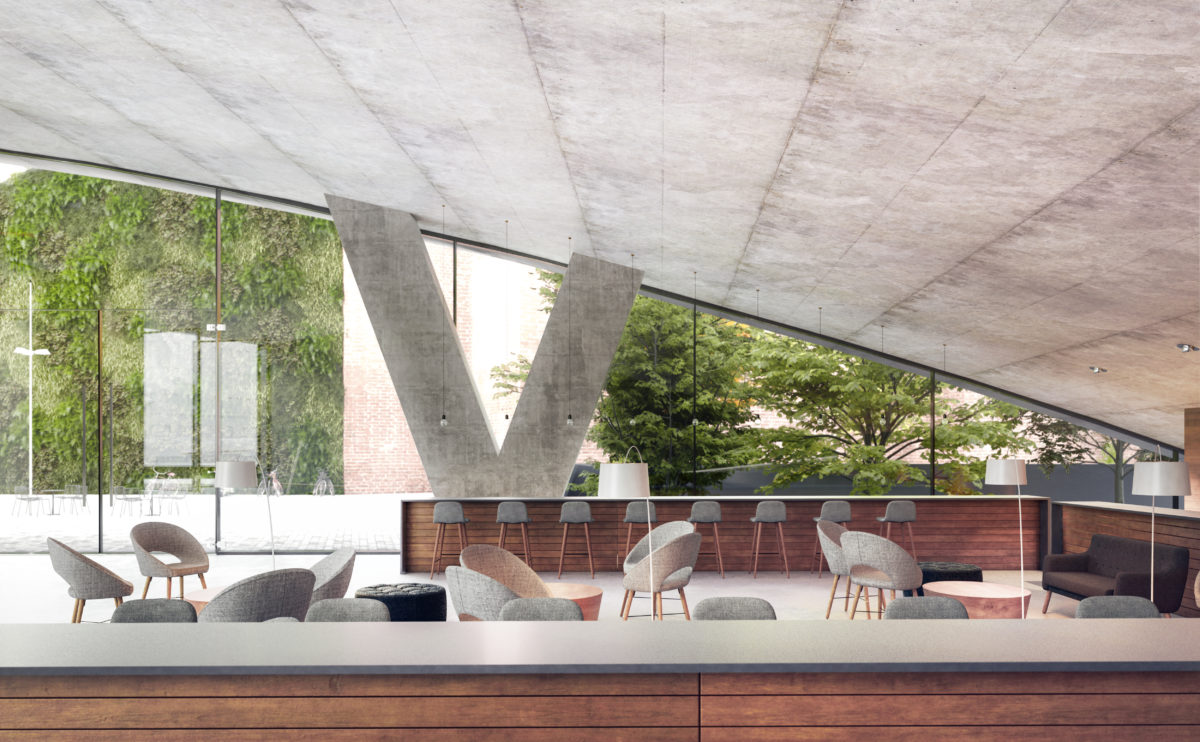
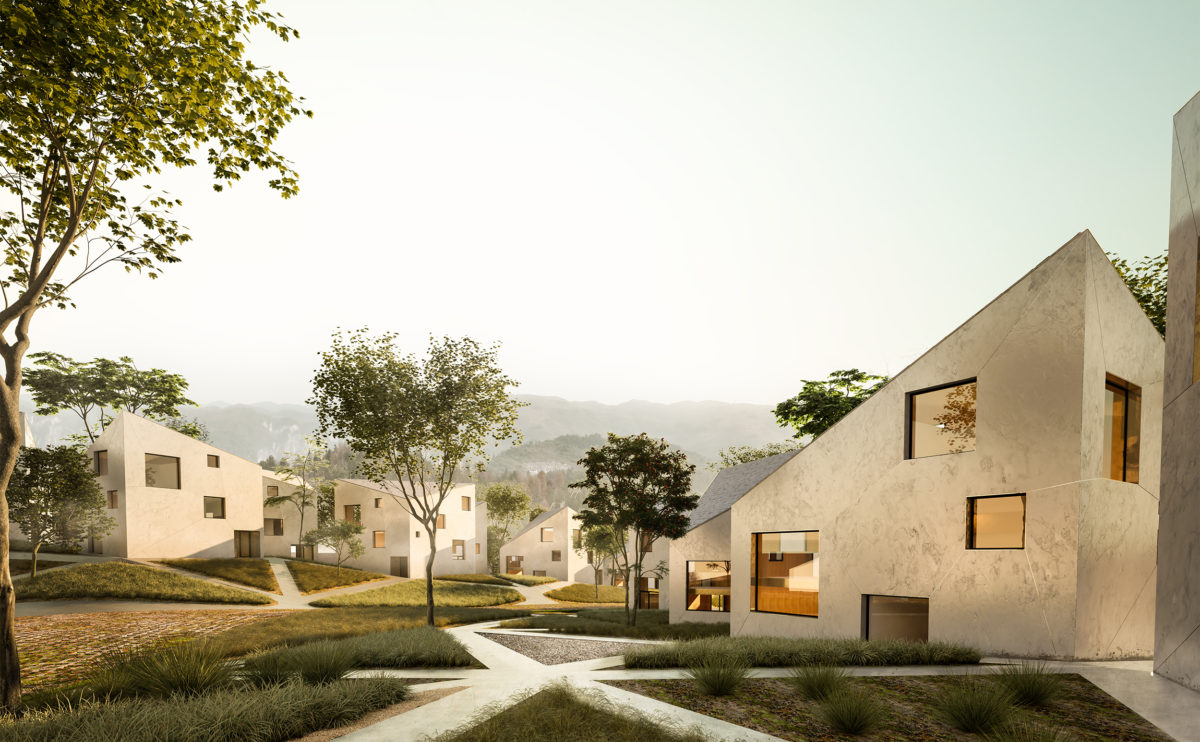
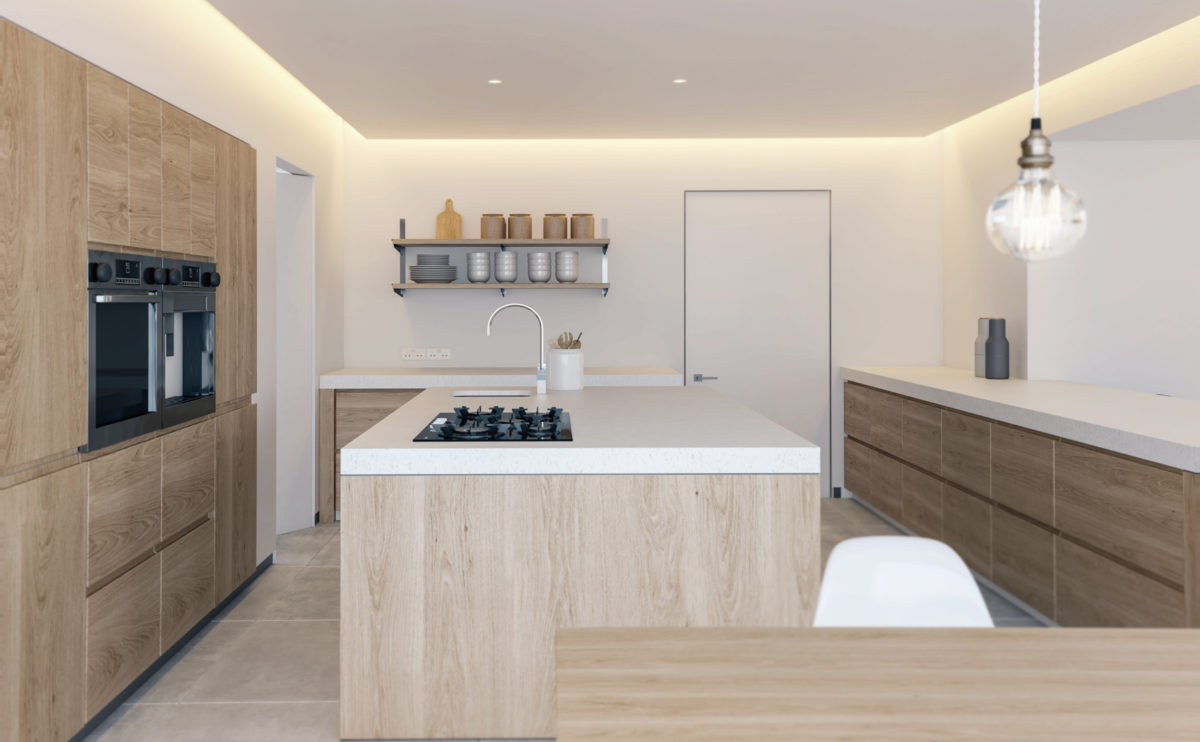
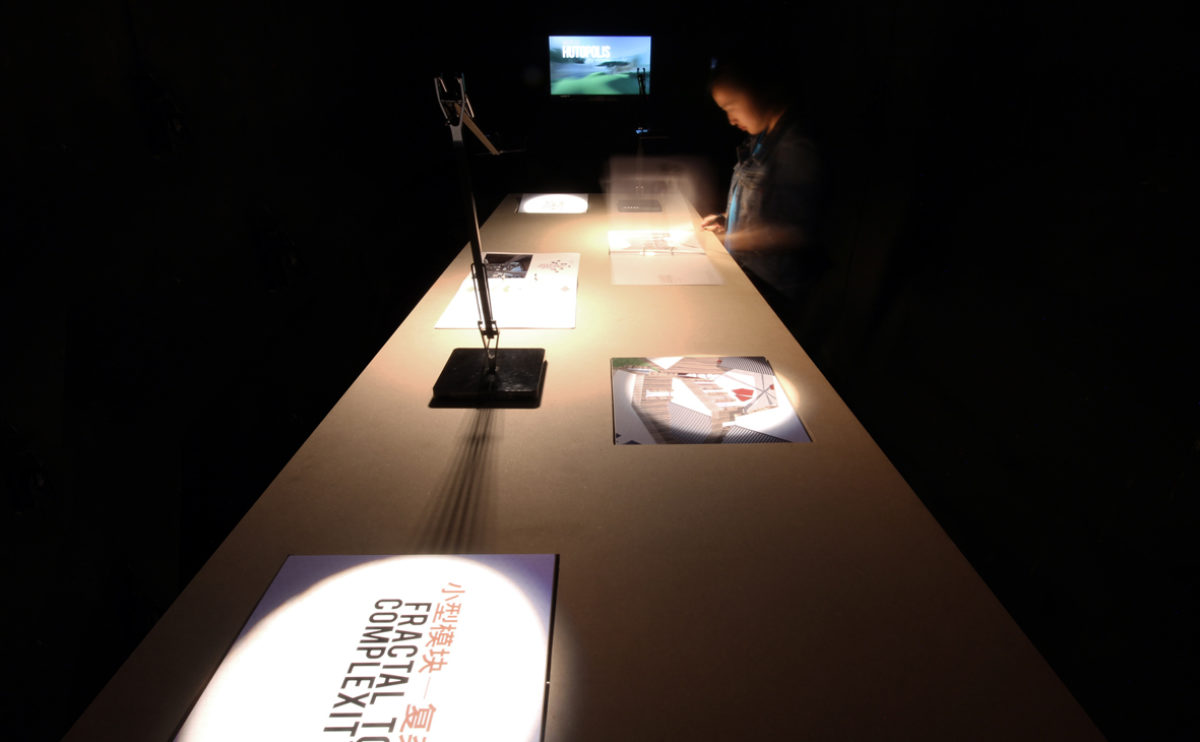
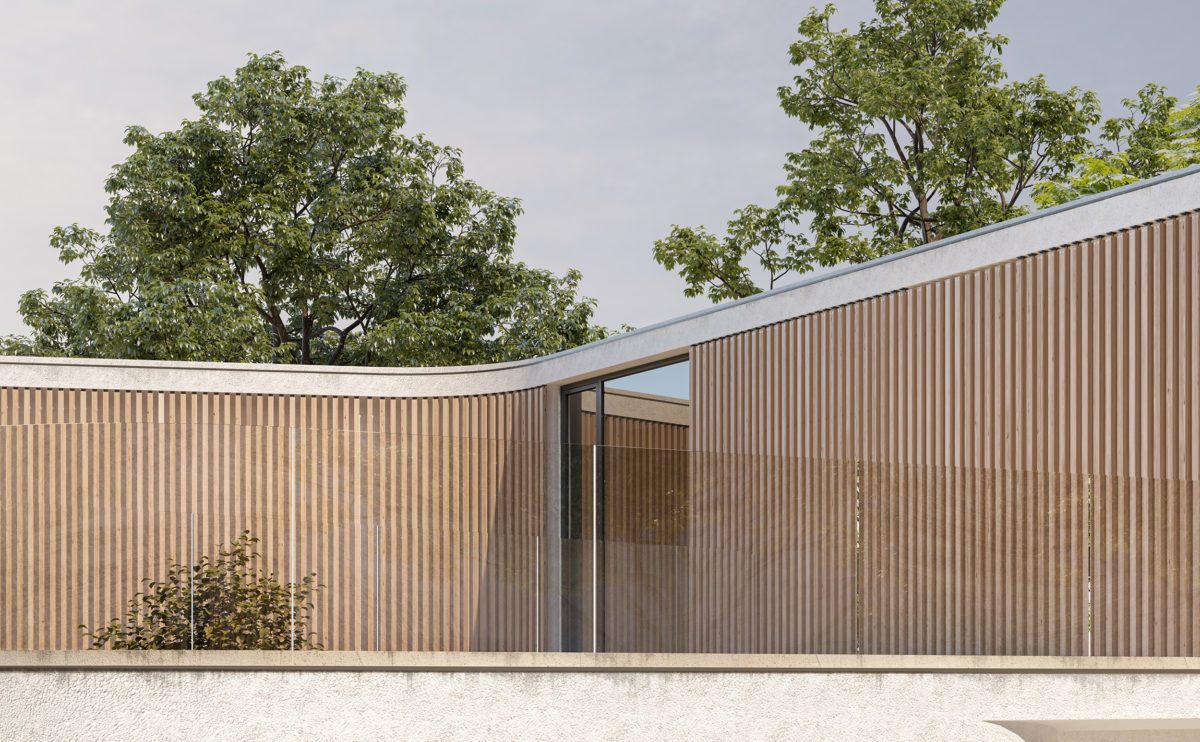
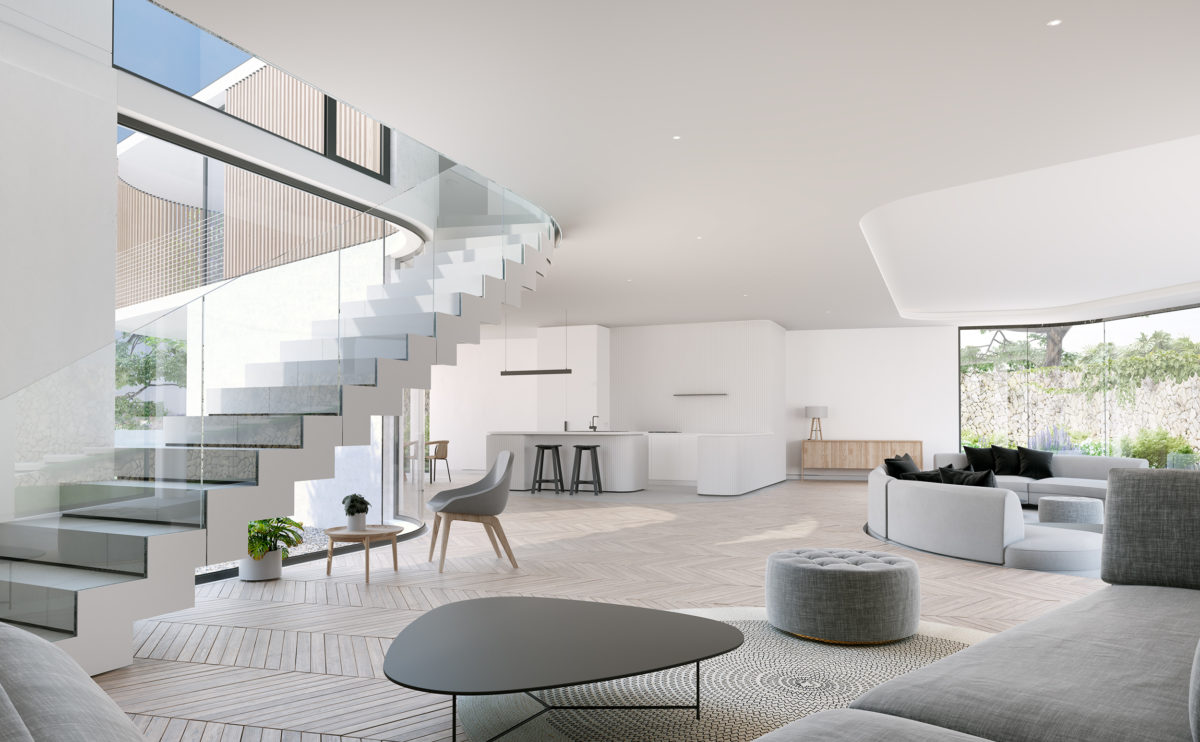
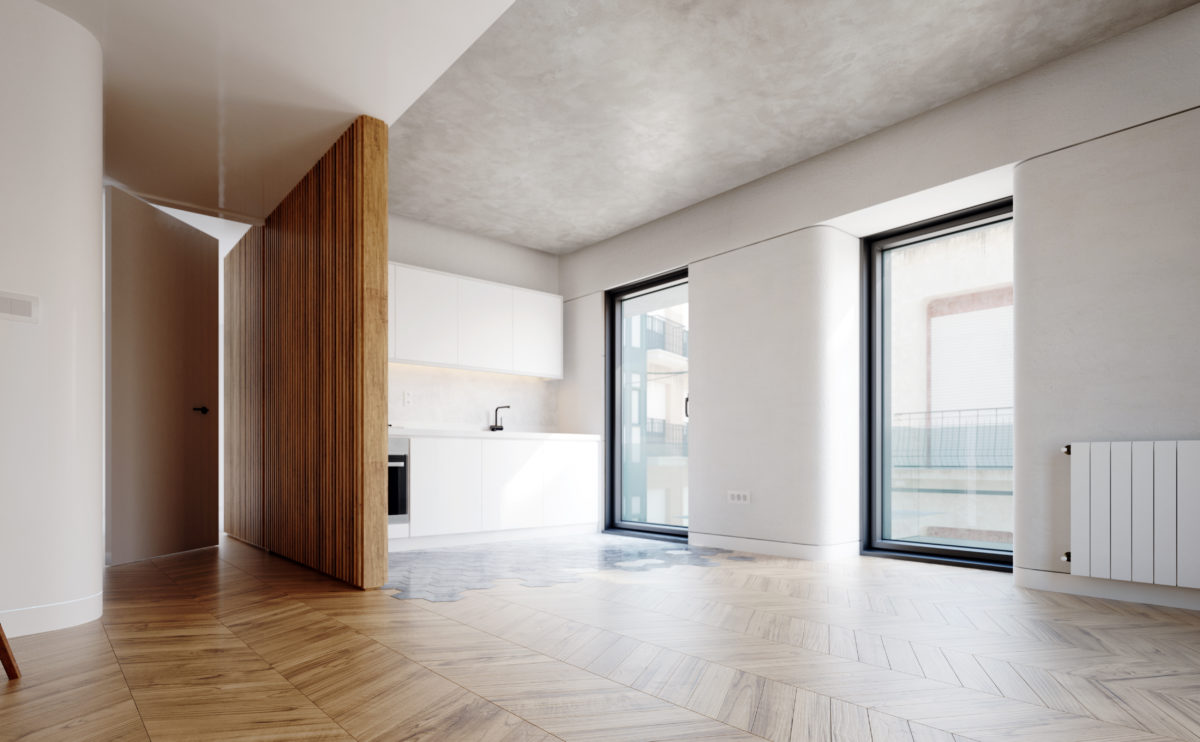
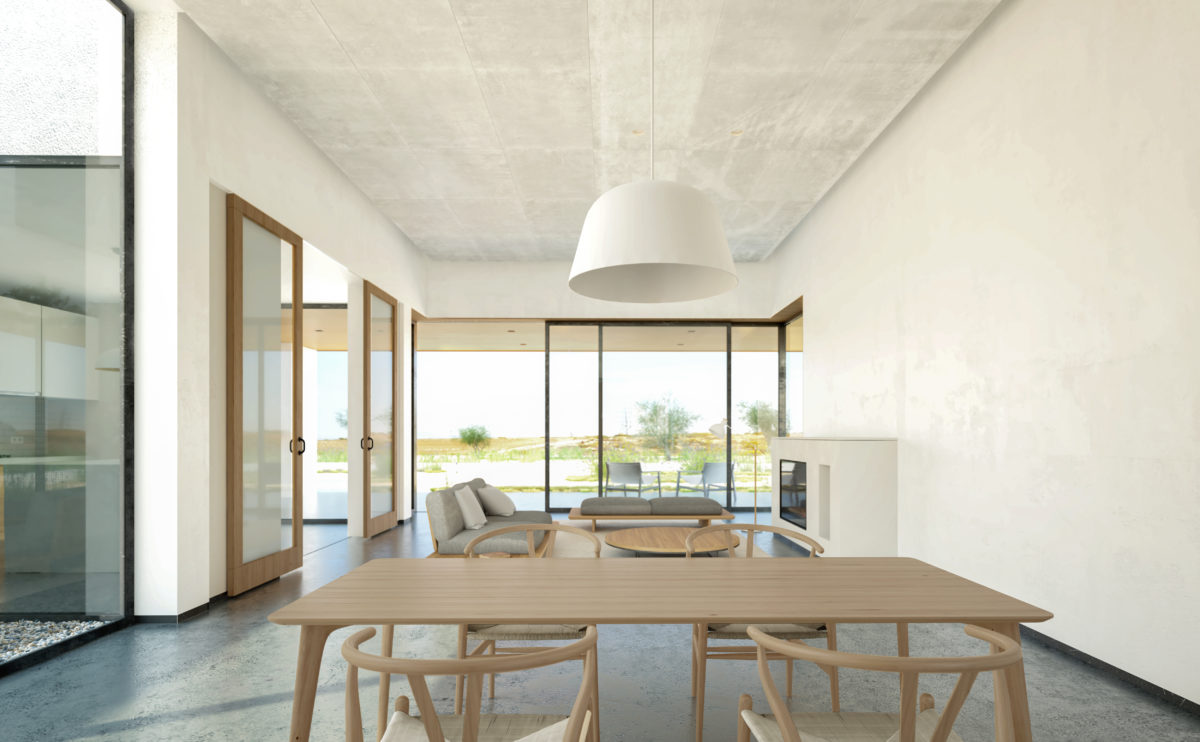
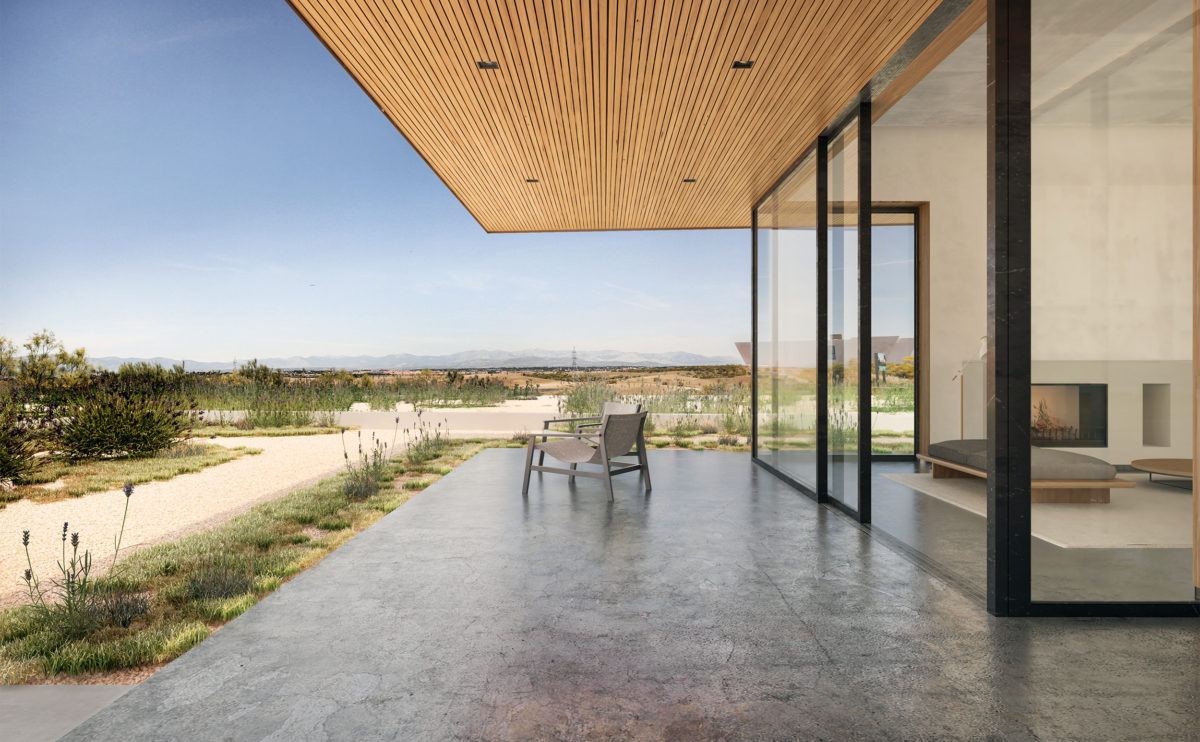
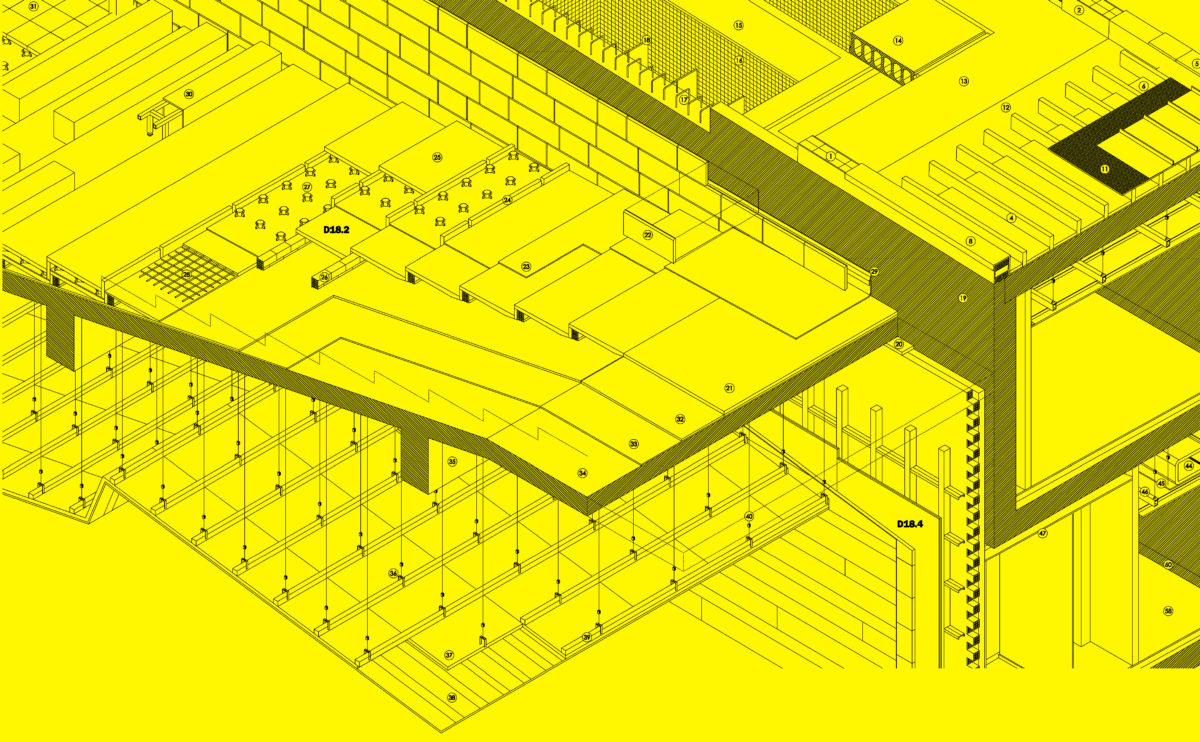
Wood is a natural building material that has been used for centuries in construction. It is a strong and durable material that is widely available and relatively inexpensive, making it an attractive choice for many types of construction projects.
Wood is often used as a structural element, such as for framing the walls and roof of a building, or as support beams and columns. Wood is also used as a finish material, such as for flooring, walls, and ceilings.
One of the key benefits of wood as a construction material is its versatility. It can be used in a wide range of applications and can be easily shaped and molded to fit the needs of a specific project. Wood is also relatively lightweight, which makes it easier to handle and transport during the construction process.
In addition to its functional properties, wood is also valued for its aesthetic appeal. It can add warmth and natural beauty to a building, and can be used to create a range of different looks and styles.
Wood is a popular and widely used construction material that has a number of modern applications in the construction industry such as framing, mass timber or cladding.
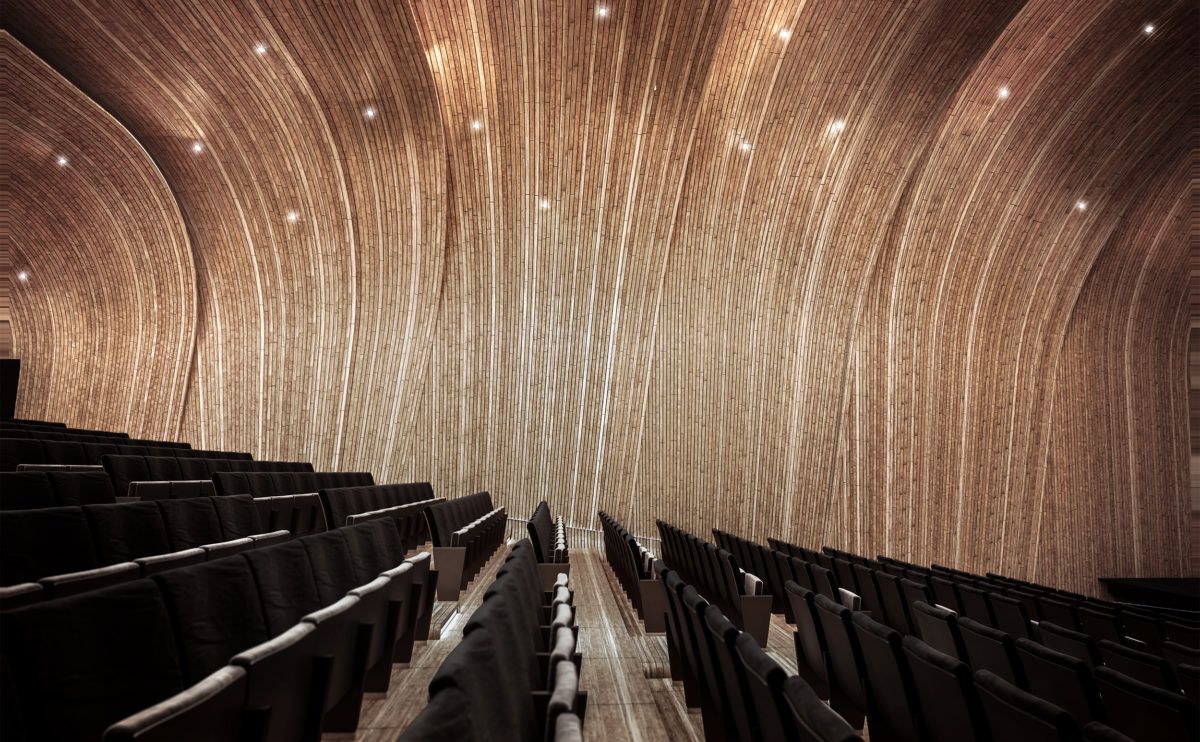
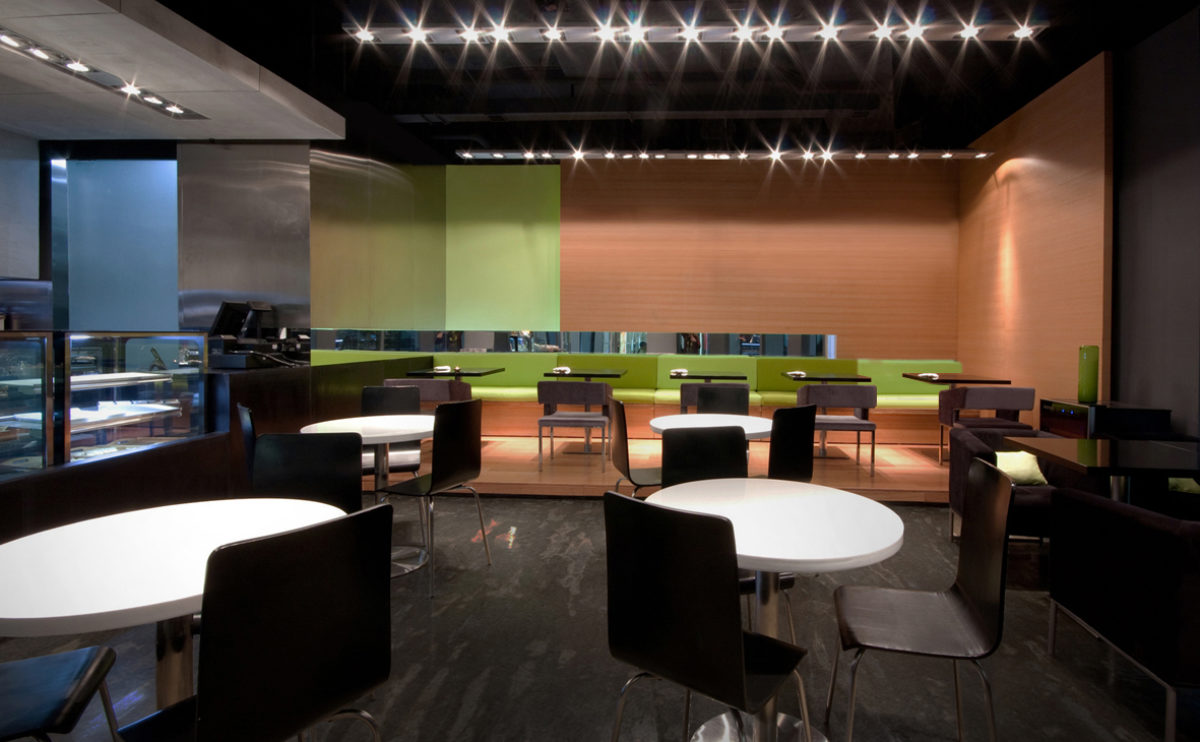
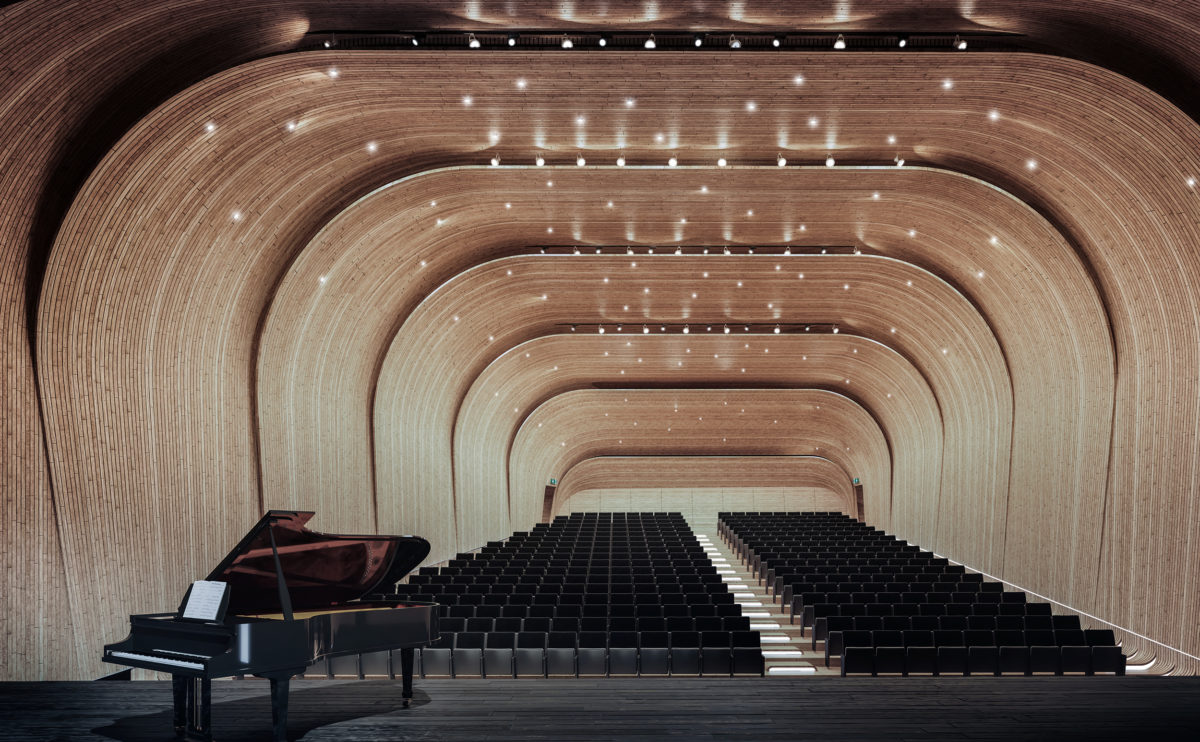
acoustical design in auditoriums
The high sonic quality of the classical amphitheatres provided the basic acoustic principles of contemporary auditoriums. As technology improves, certain acoustic design principles are augmented. For example, the geometry of the stepped stalls can now be retracted and lifted using air castor technology.
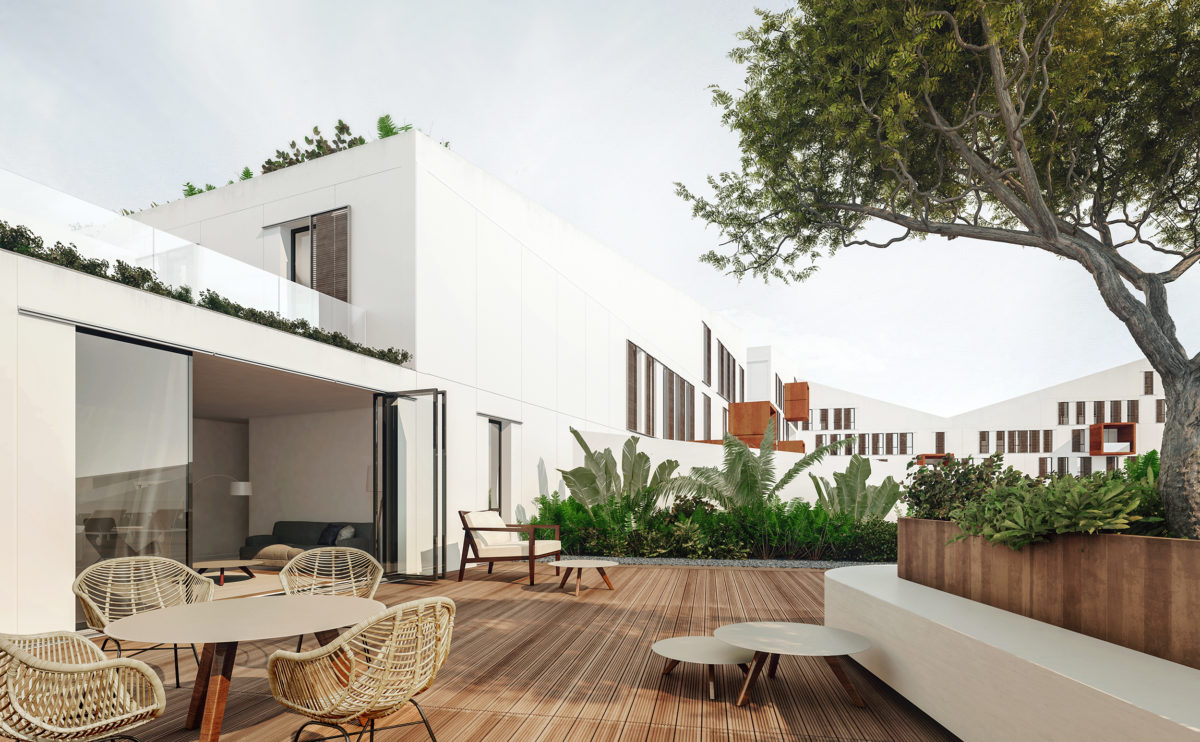
Harvest Home awarded by the IaaC
The self-sufficient house Harvest Home has been given an award in the ‘2nd Advanced Architecture Contest’, an international competition organized by the Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia.
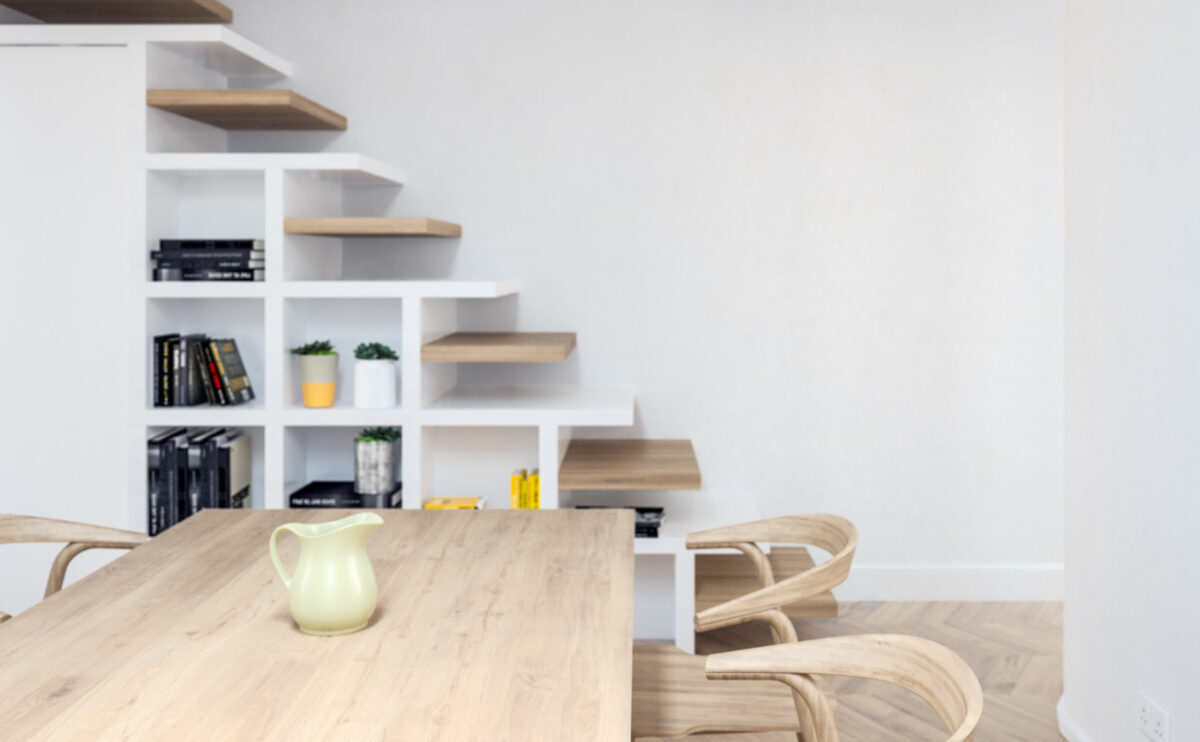
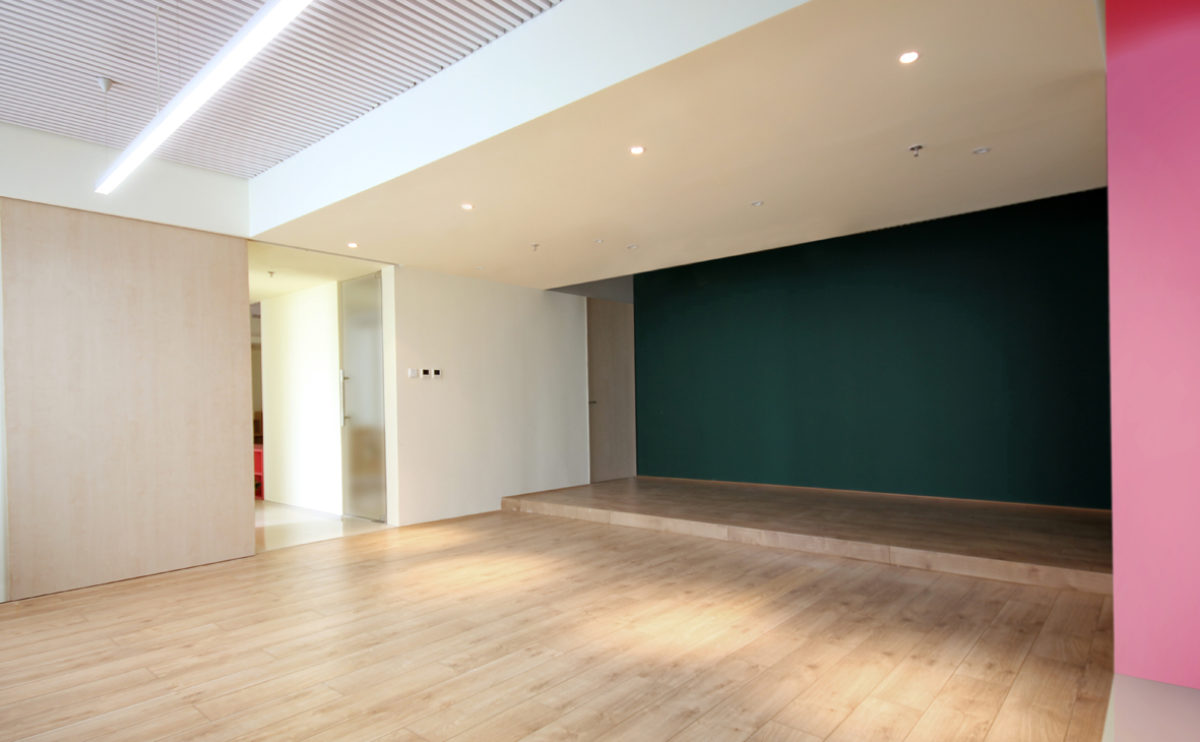
social club completed in Tabuyo
The works for the interior design of this social club in Tabuyo have been recently completed. Characterized by simple materials and indirect lighting, this project comprises a multipurpose room, a dining room, storage, and toilets.
possible architecture
The project for a music centre in Soria has been selected for inclusion in the ‘Arquitecturas posibles’ exhibition organized by agoras.arq. The exhibition will be held in the MUVa Museum, Santa Cruz Palace, Valladolid, Spain, from October 3rd.
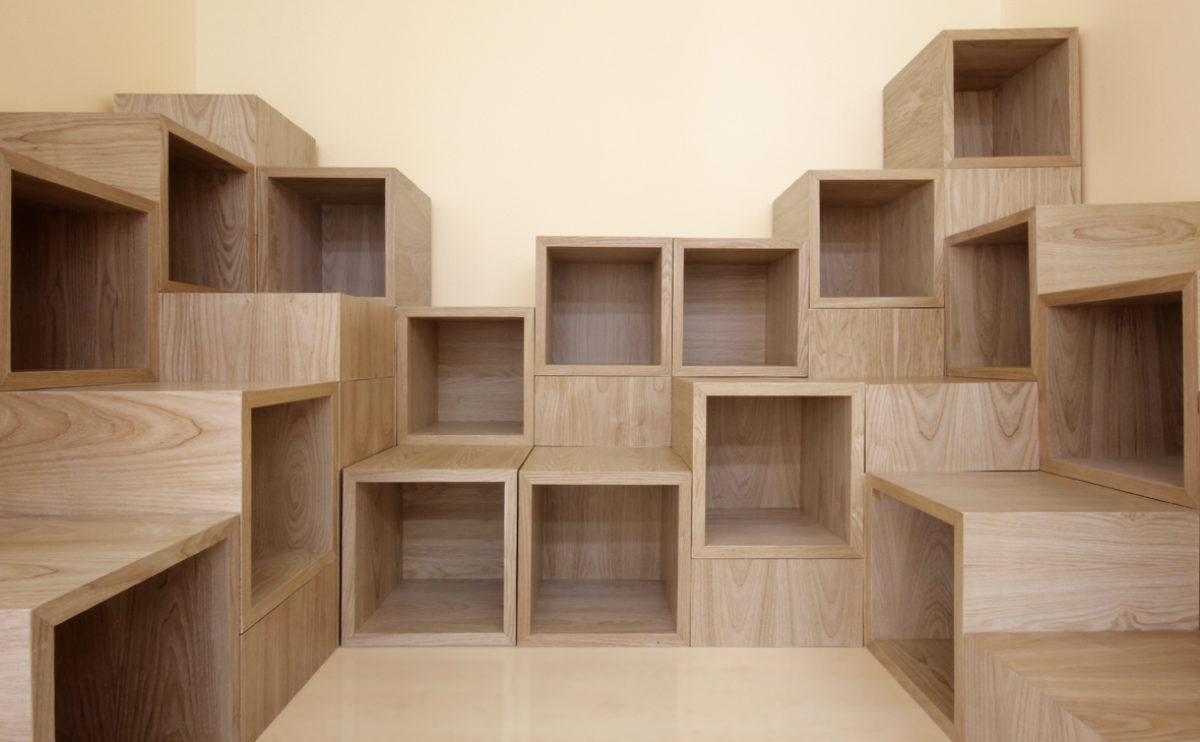
physical models
Physical models are copies to scale of structures or buildings ‒ with the aim to study design features, analyse a building or space within its context, and convey conceptual ideas.
using authentic eco-friendly building products
Advanced technologies in materials engineering continuously pave the way for the manufacturing of synthetic materials. Building typologies which once exhibited natural and organic surface materials are now replaced with composites, plastics and resins. However, specifications on the form, particularly on the façade itself, channel directly into its users the perception, character and function of the […]
finishes specification
Finishes specification involves detailing a list of all the materials in the final parts of the project. The file contains commercial products available in the market following technical, functional, aesthetic, and economic criteria ‒ price and maintenance costs.
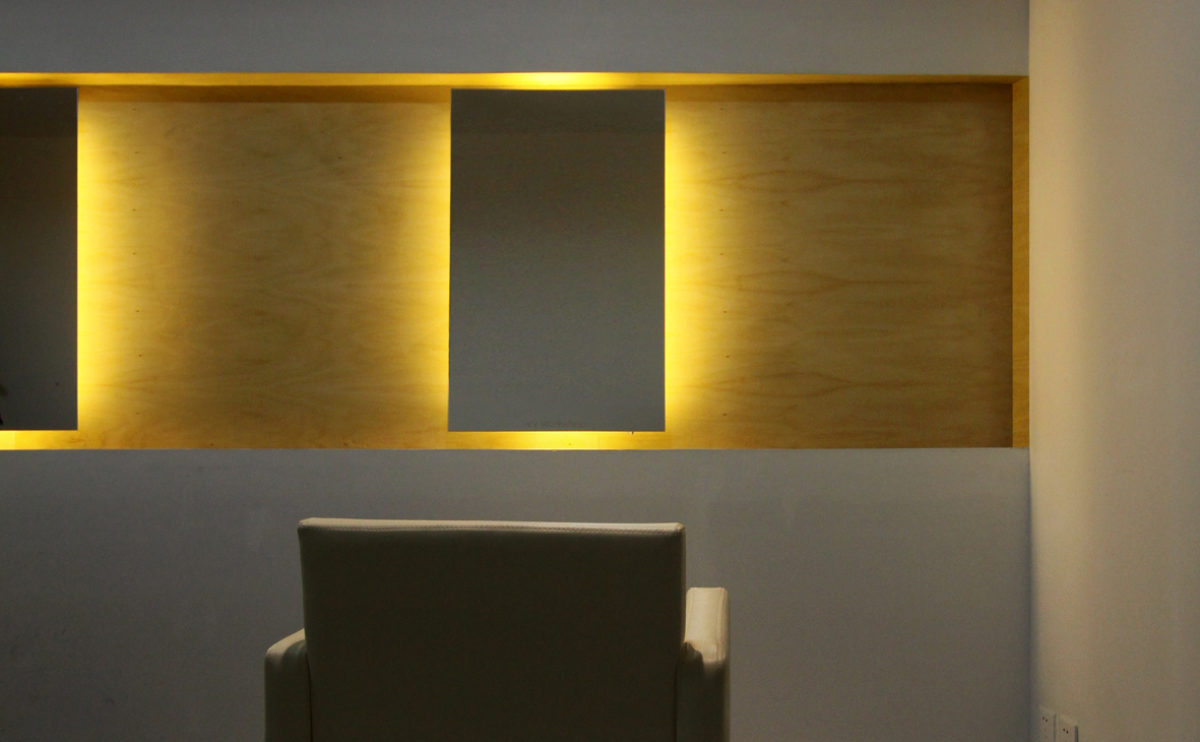
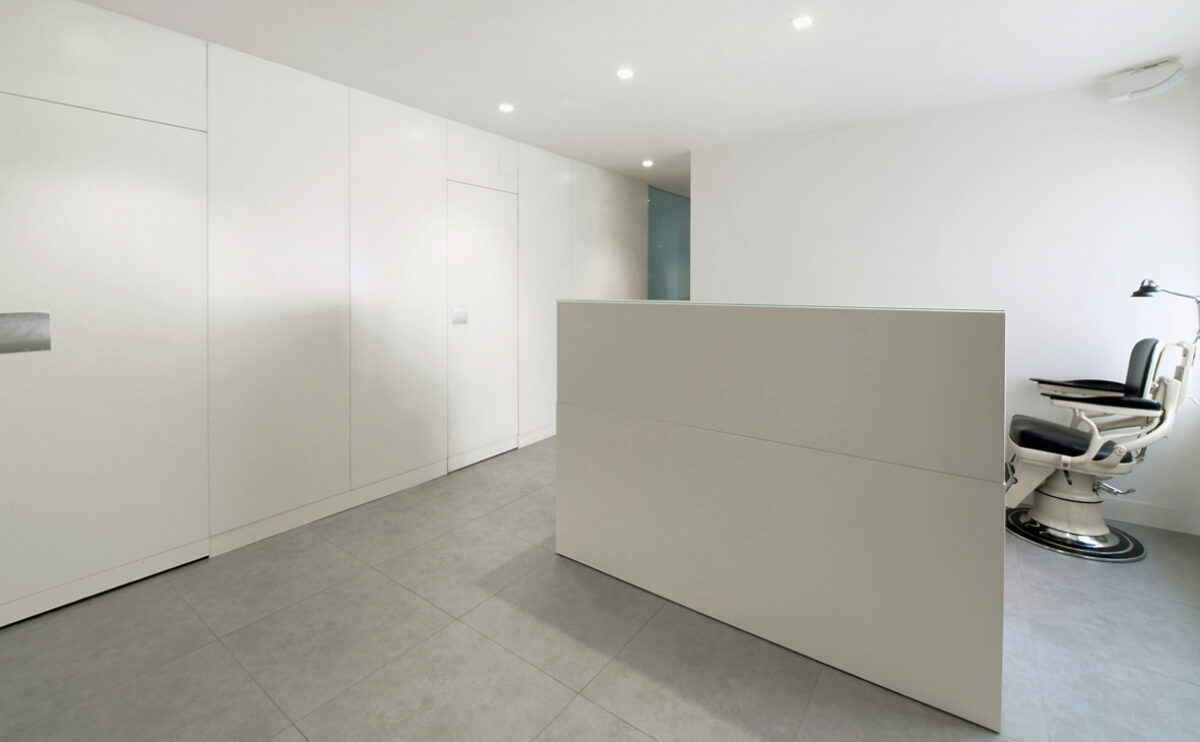
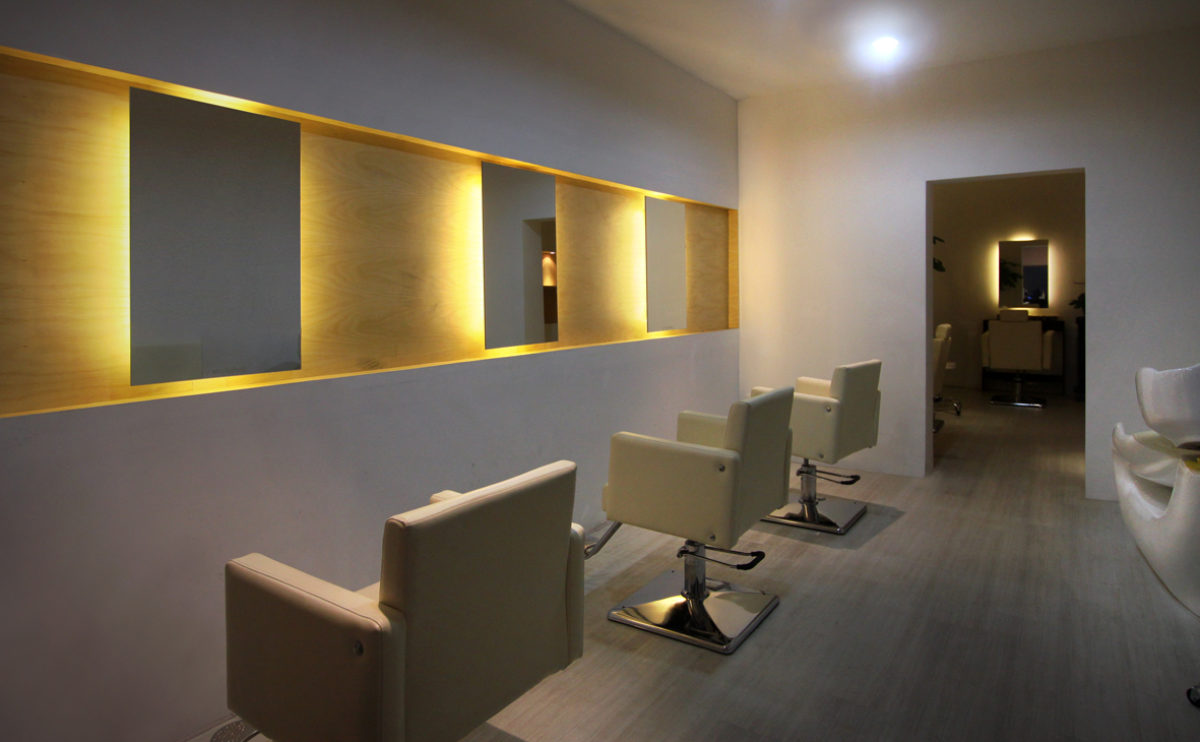
W salon opening
The interior of a hair salon in Beijing designed by AQSO has been recently completed.
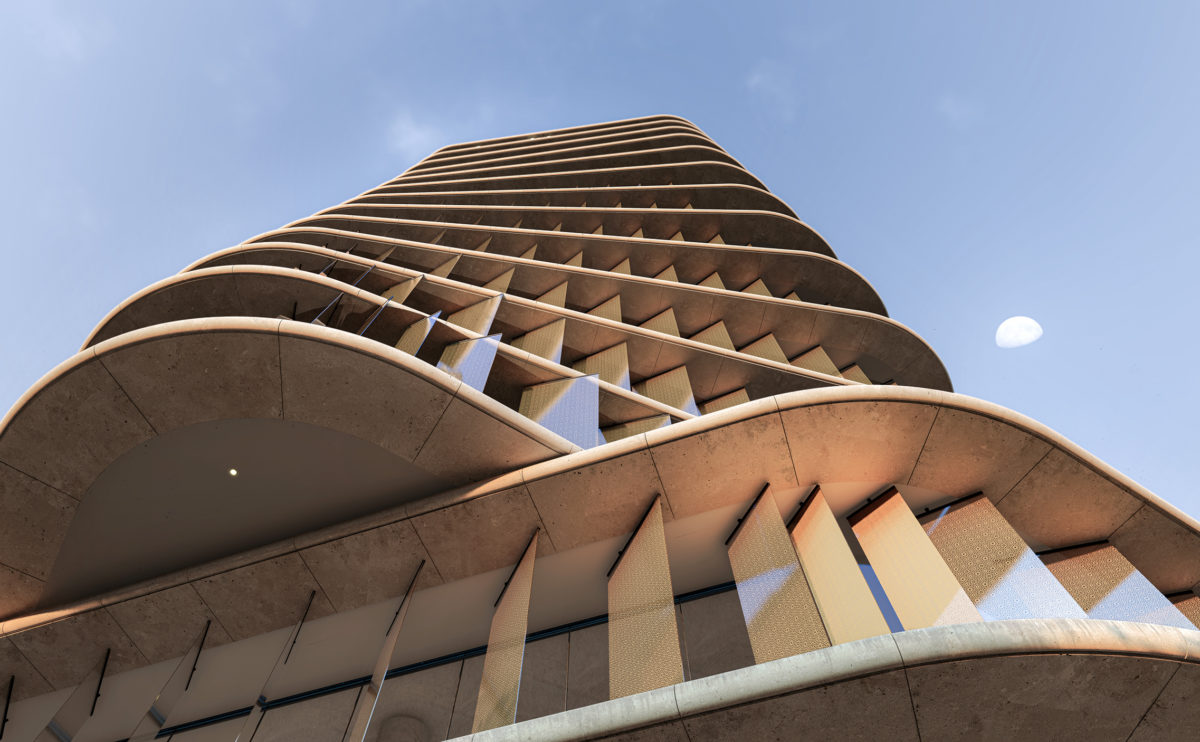
the illusion of weightless architecture
High-tech advancements in structural engineering give birth to the reality of intricate architectural designs. Building typologies now exceed what was once compromised because of traditional methods. The advent of Information Age will continuously break ground for the optimisation of structural systems. As innovations surge, the potential for growth in the industry provides more opportunities.
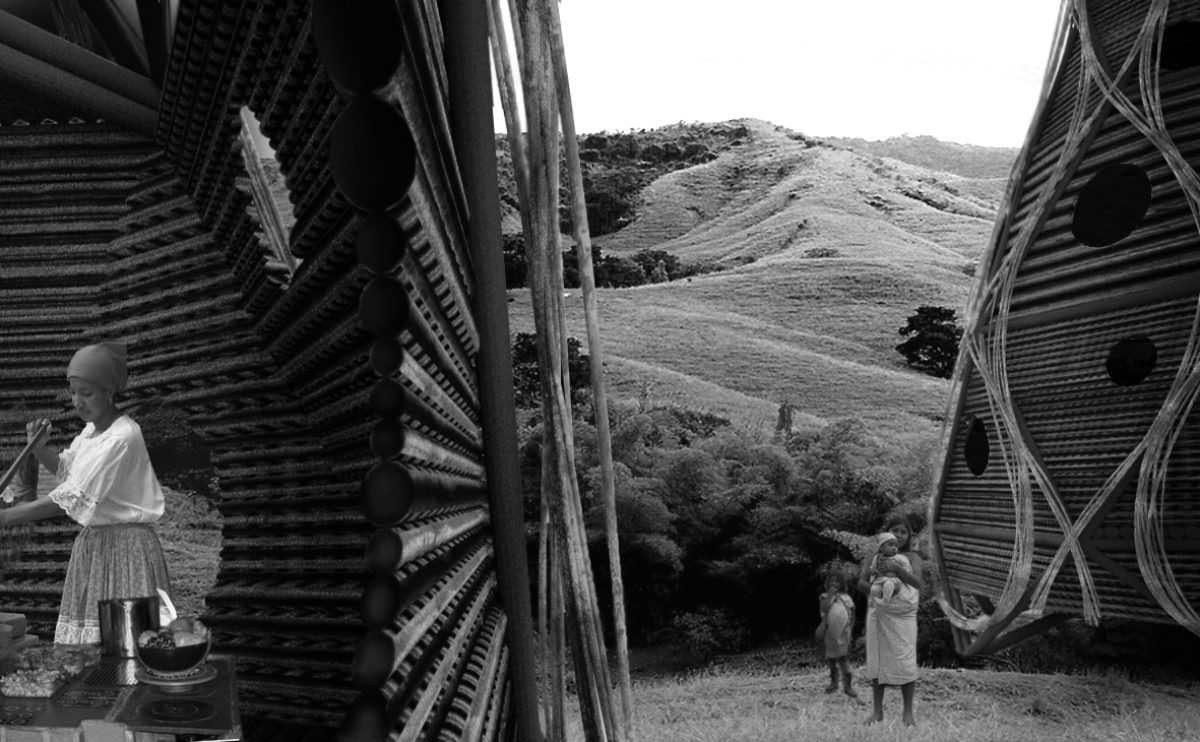
self-fab house
This publication features a selection of experimental projects about self-fabrication, with articles written by Vicent Guallart, Lucas Capelli and Willy Müller among others.
building products for sustainable design
As architects, we have a social responsibility to promote environmental equality. To fight climate change, we need to cut back on energy consumption costs for buildings. We start by designing for sustainability.