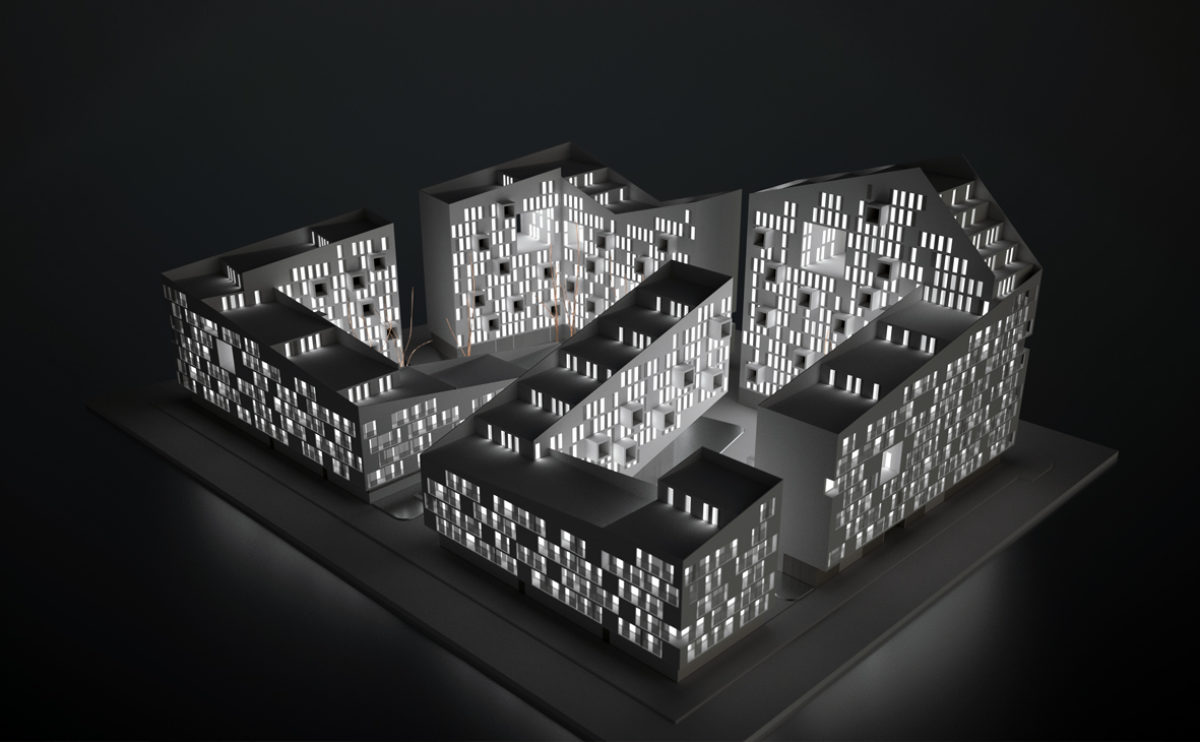
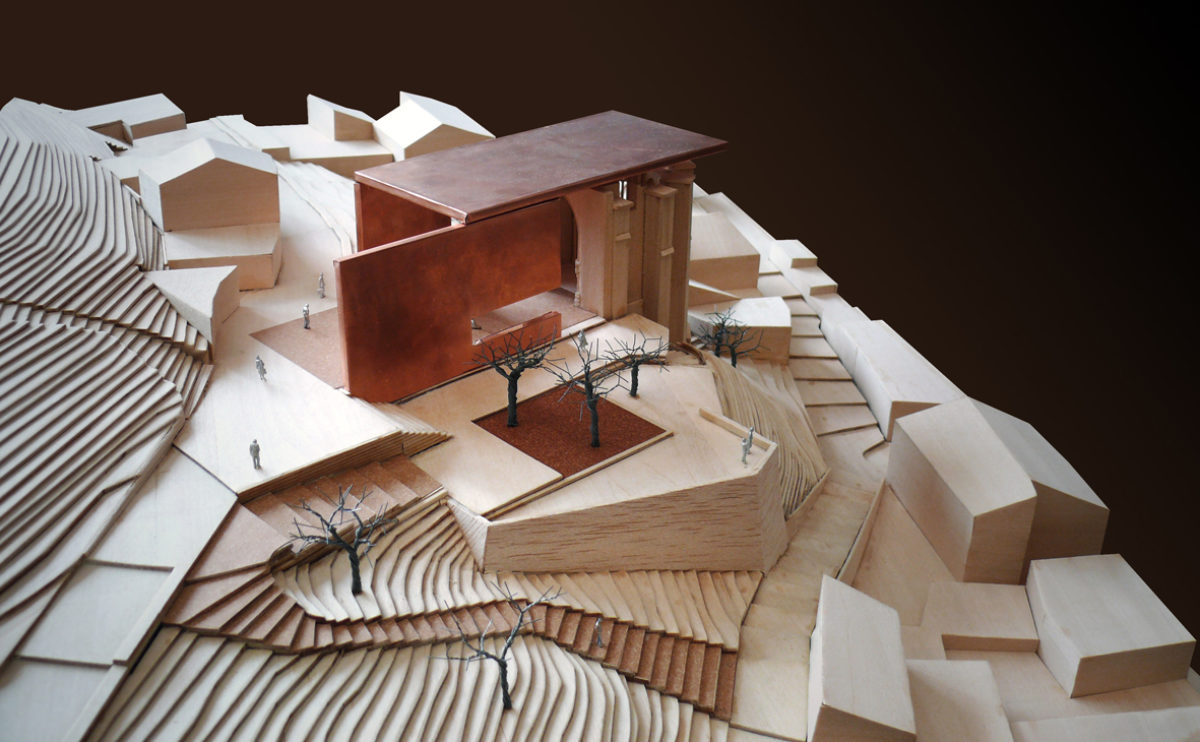
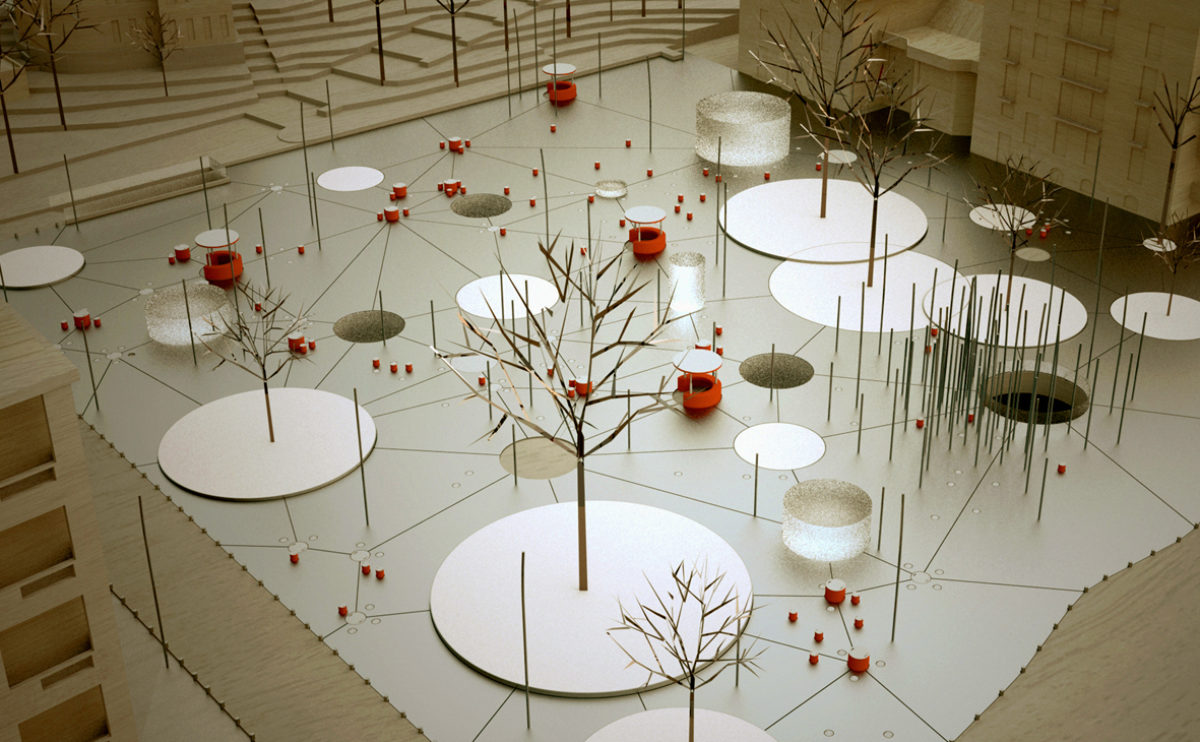
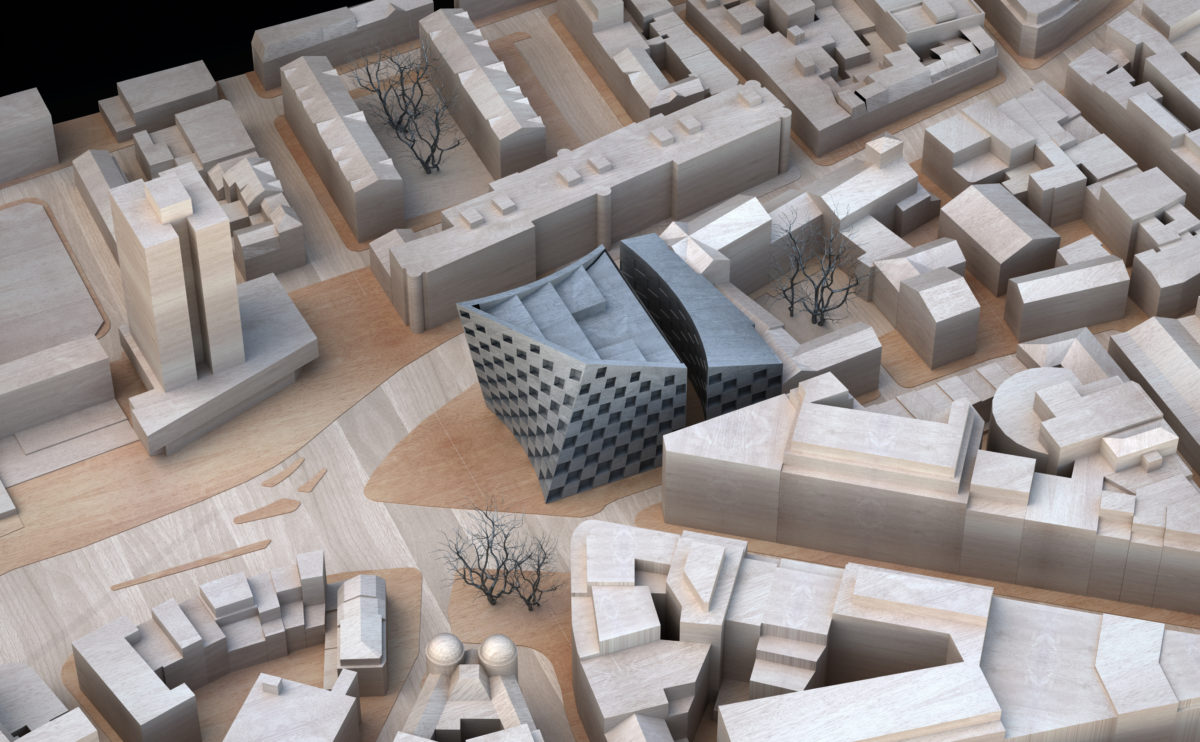
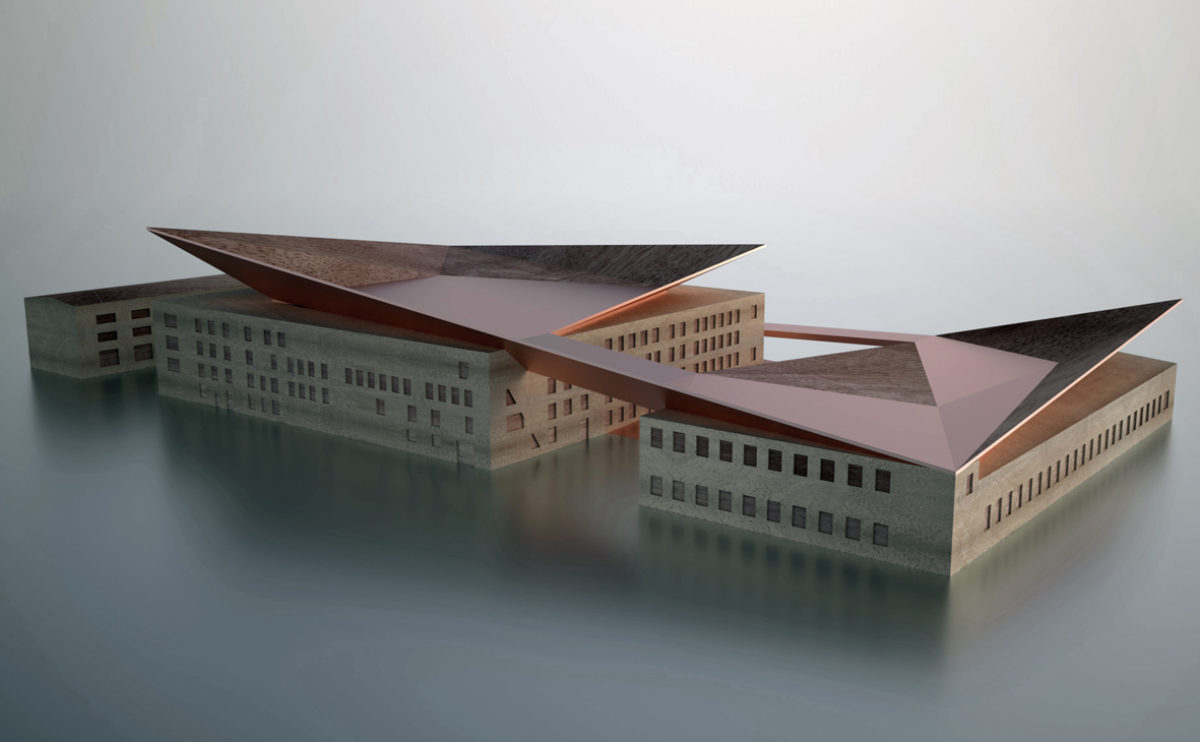
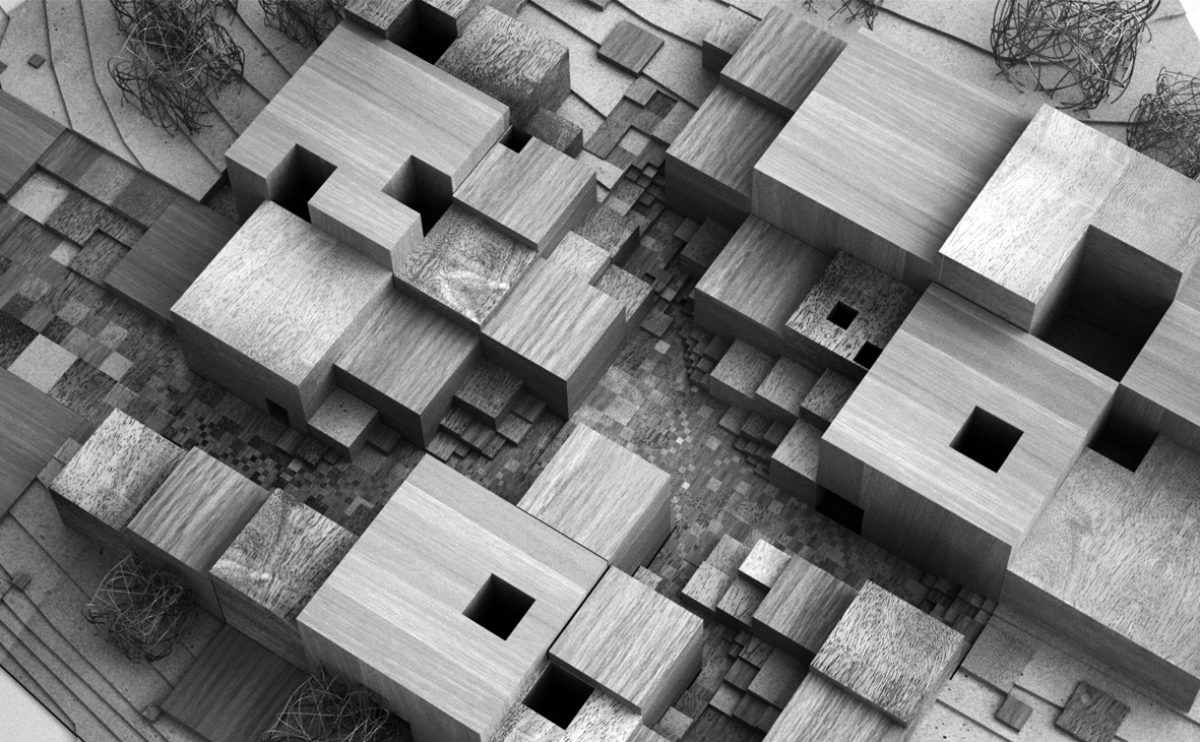
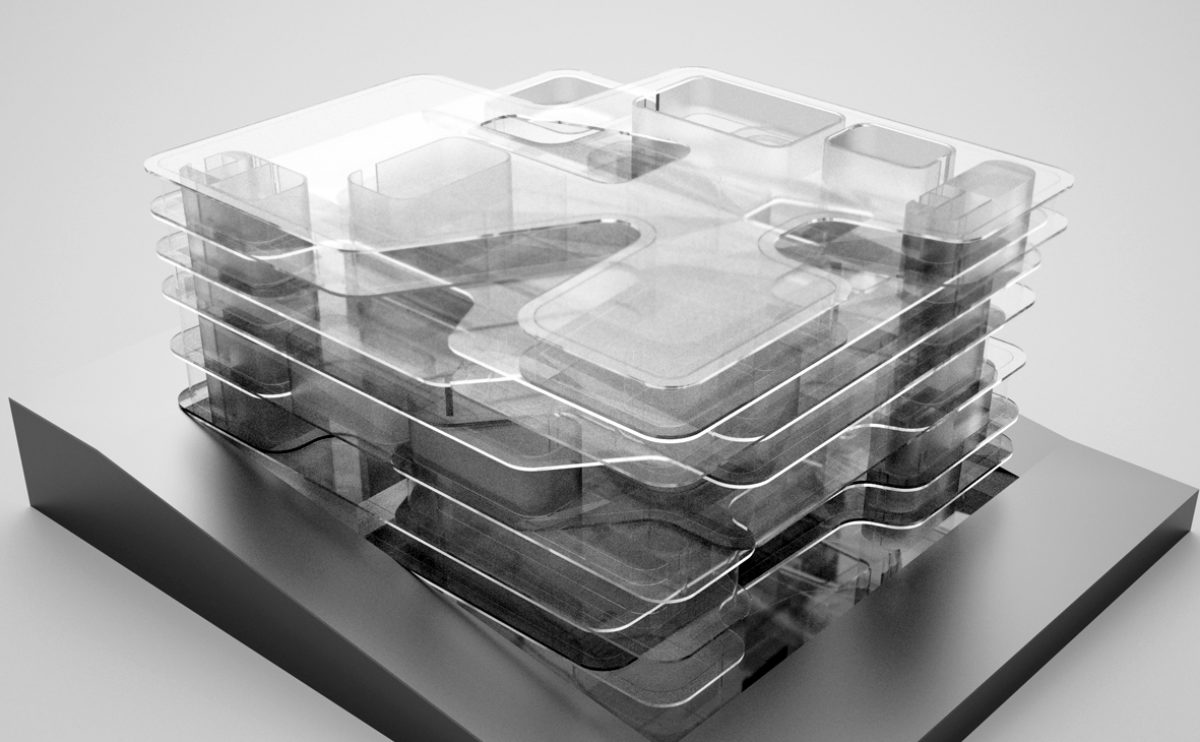
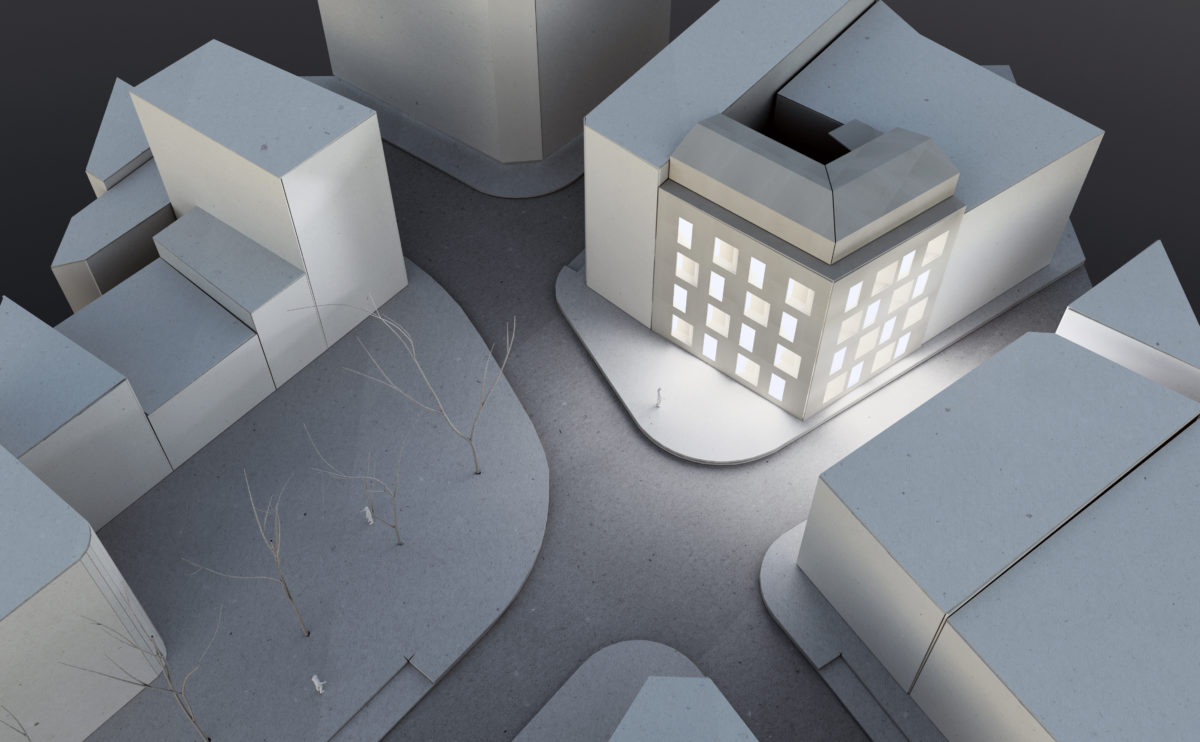
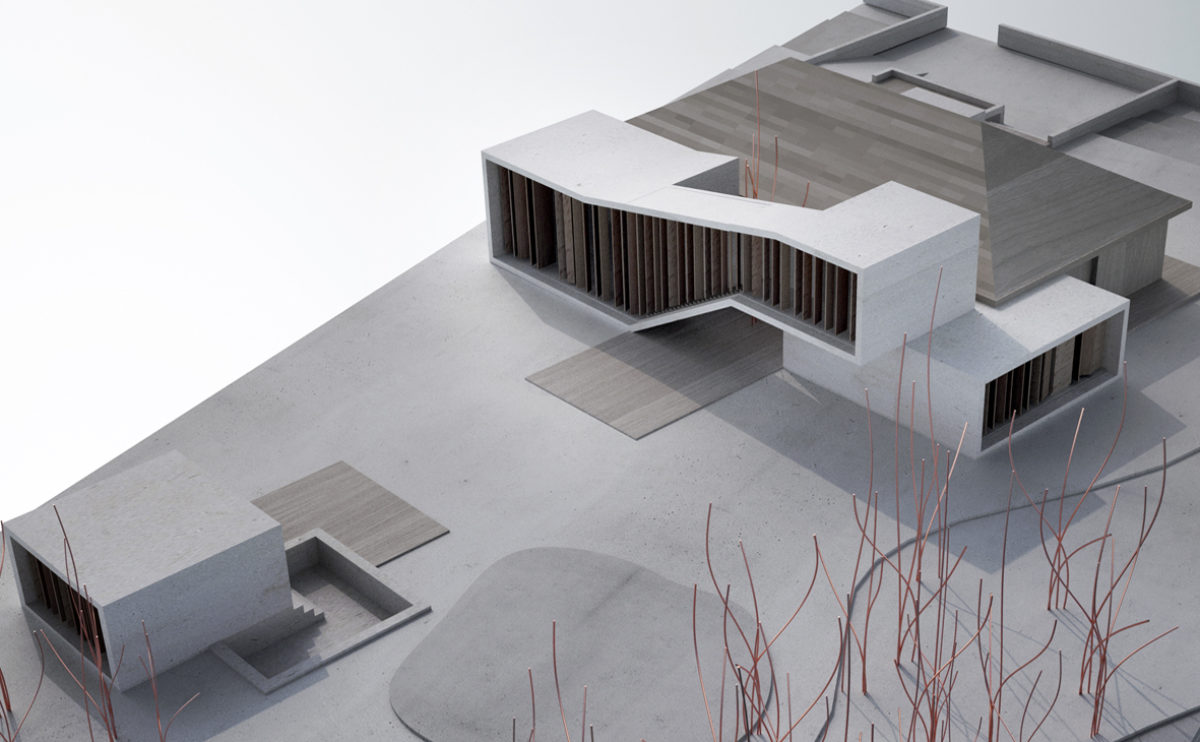
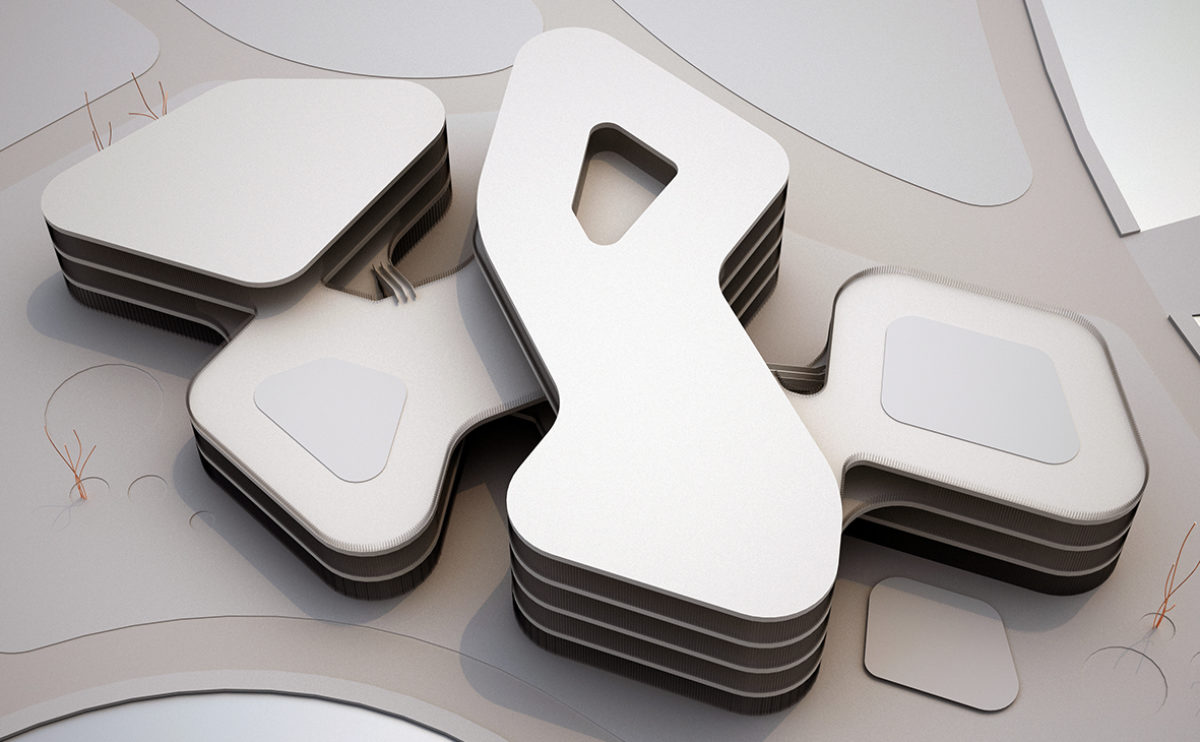
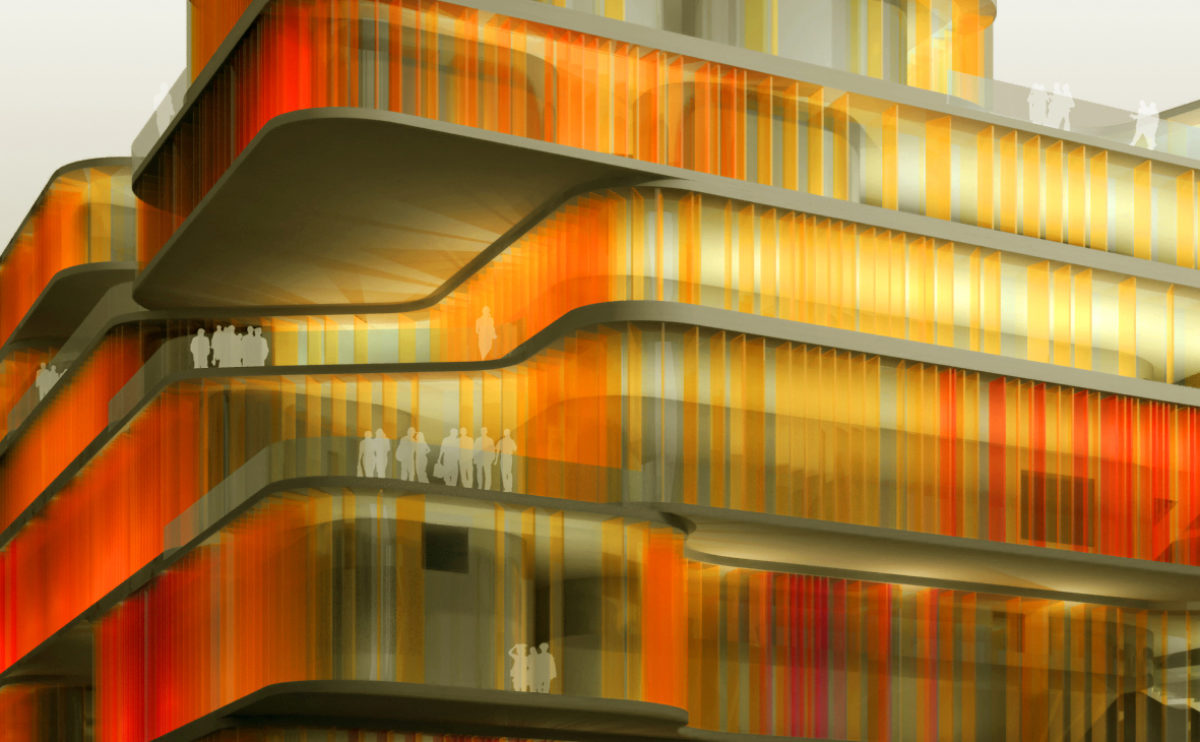
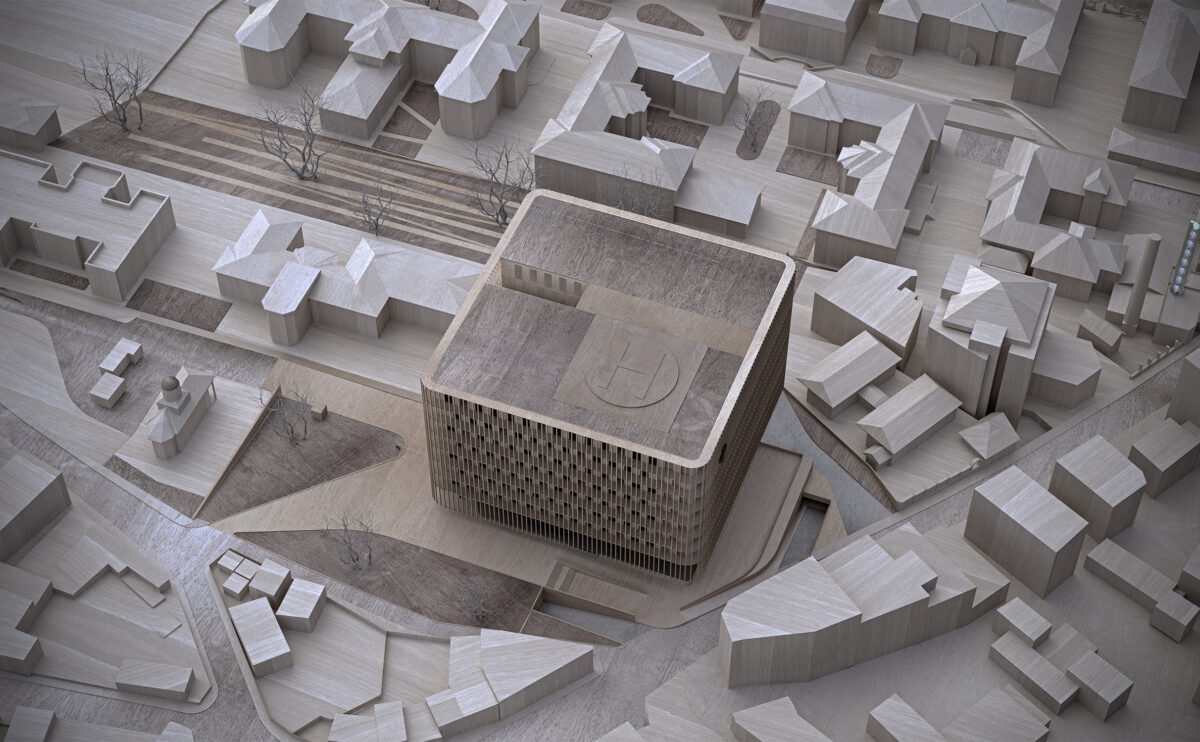
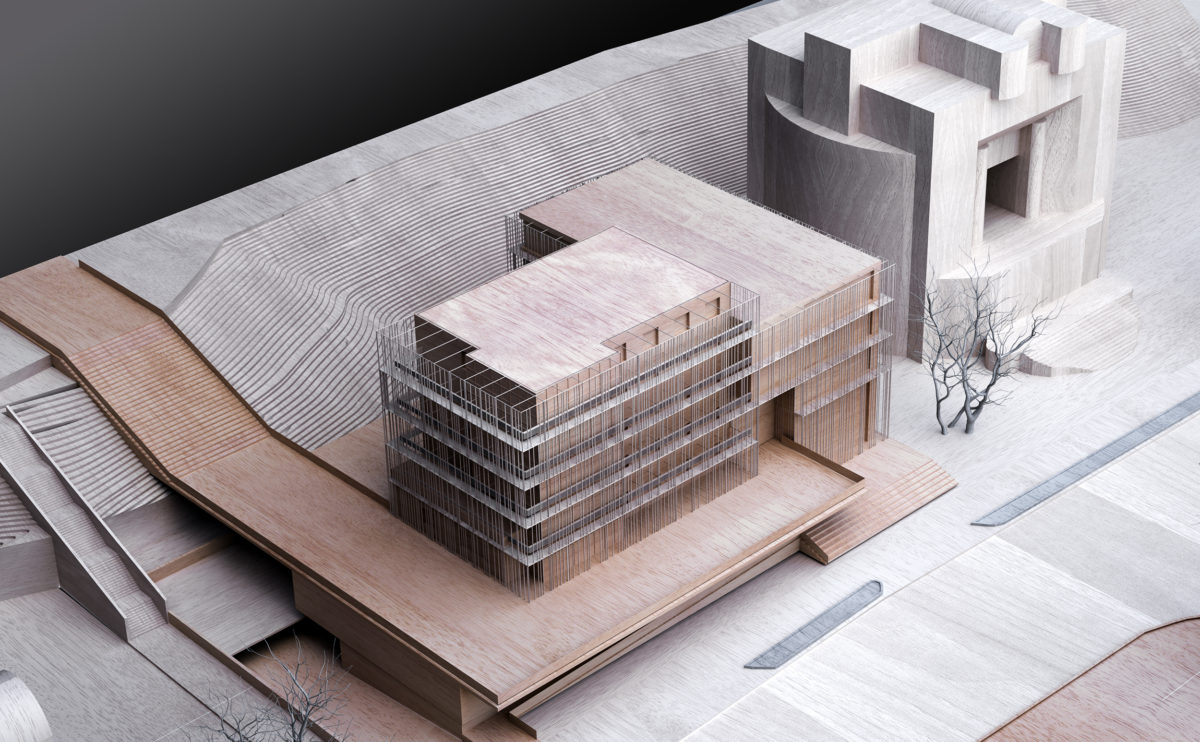
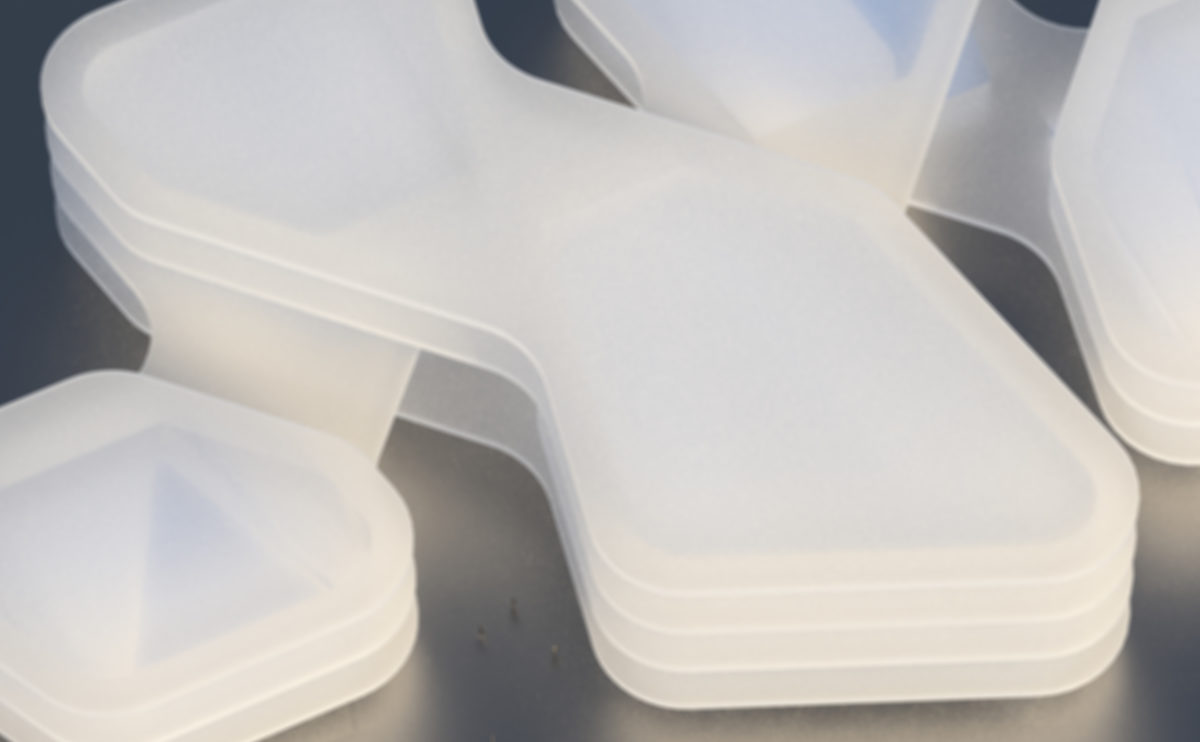
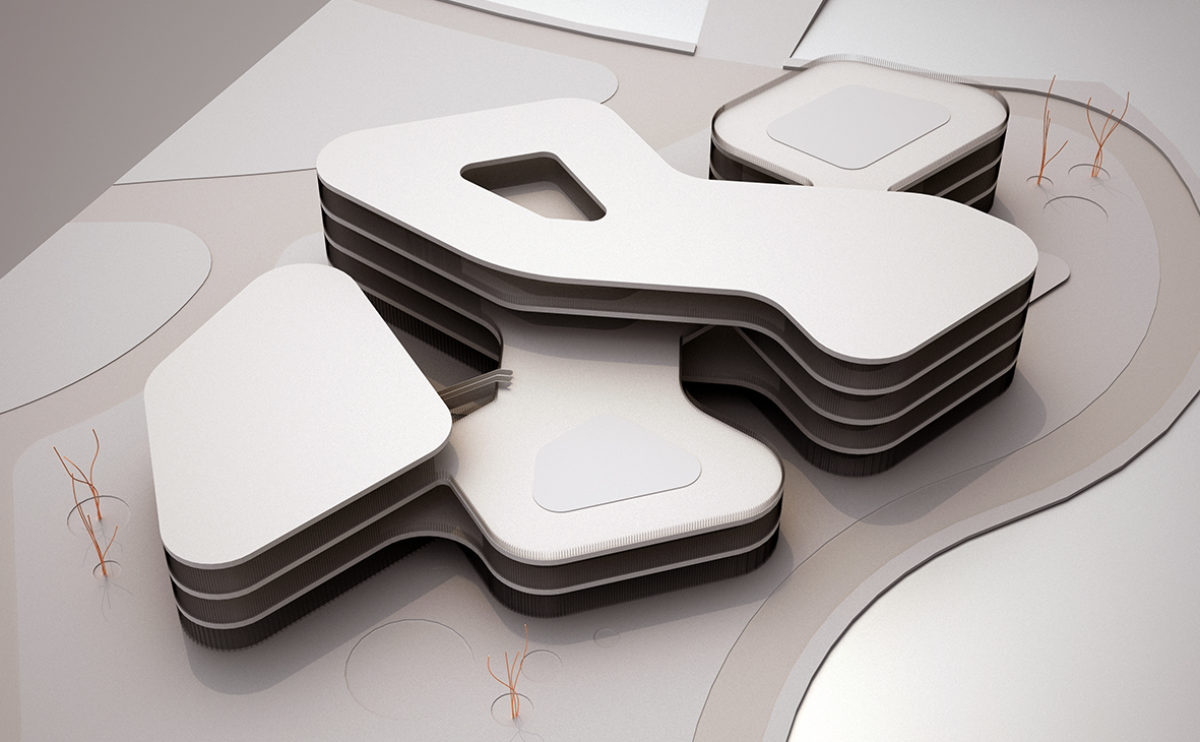
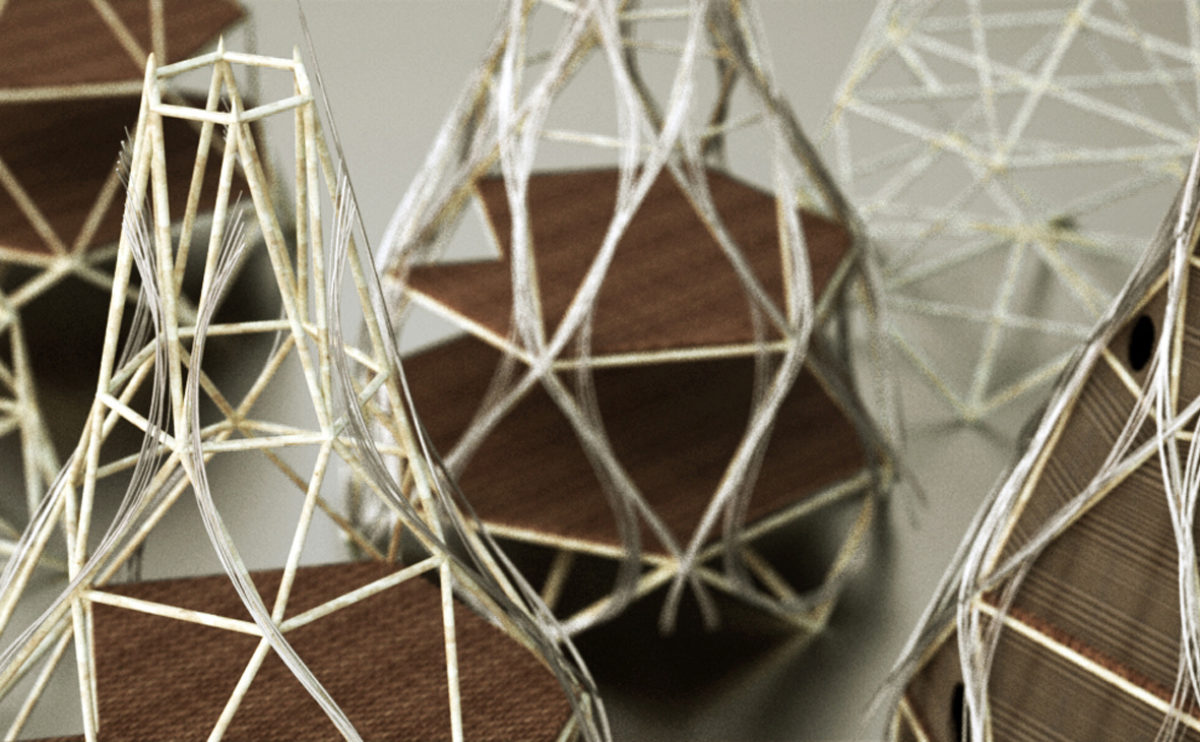
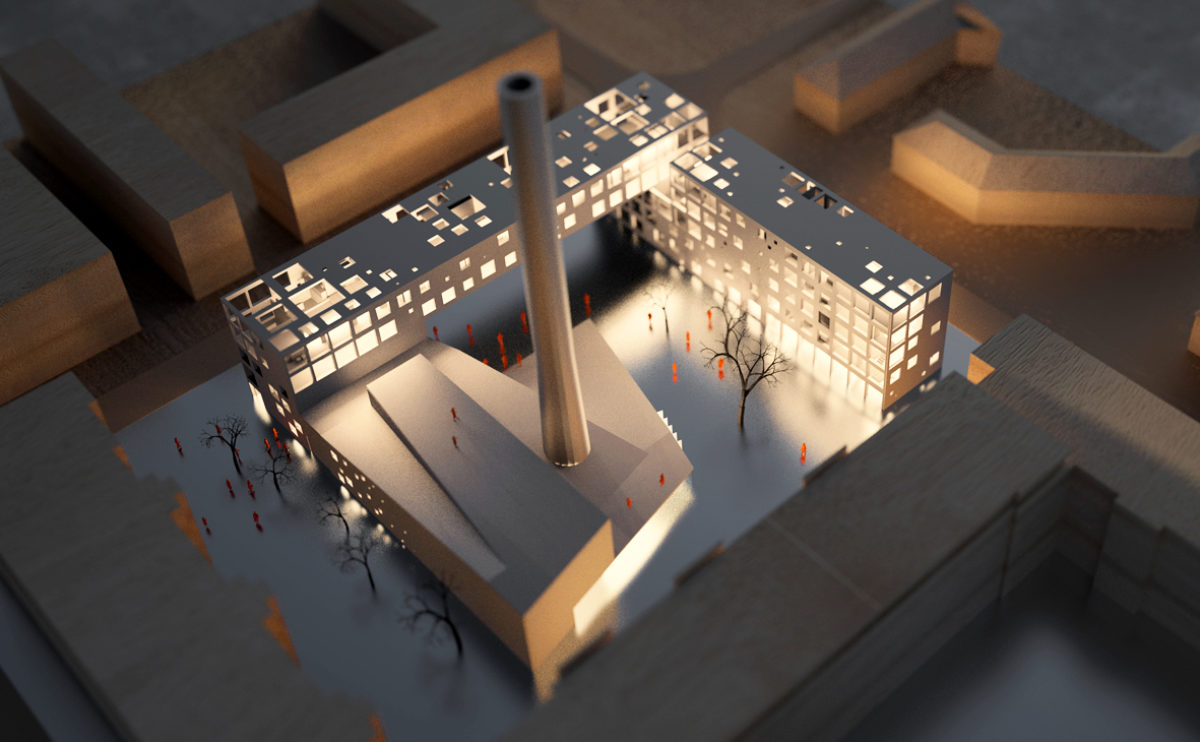
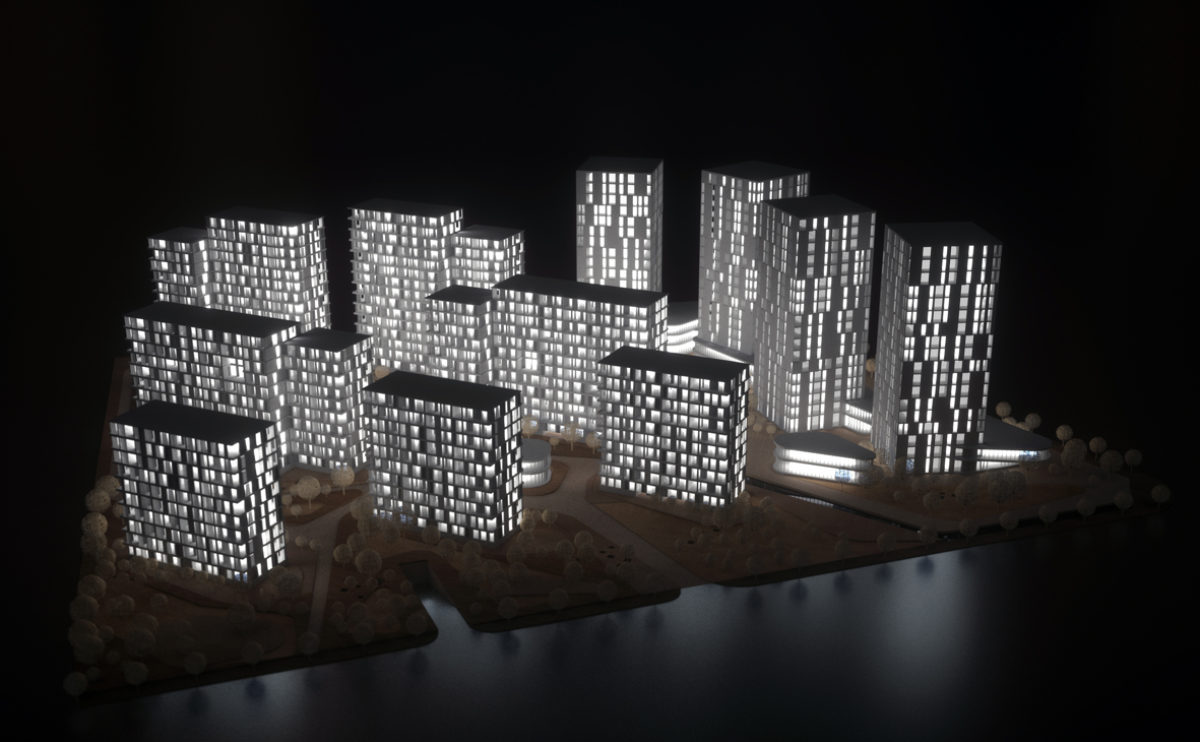
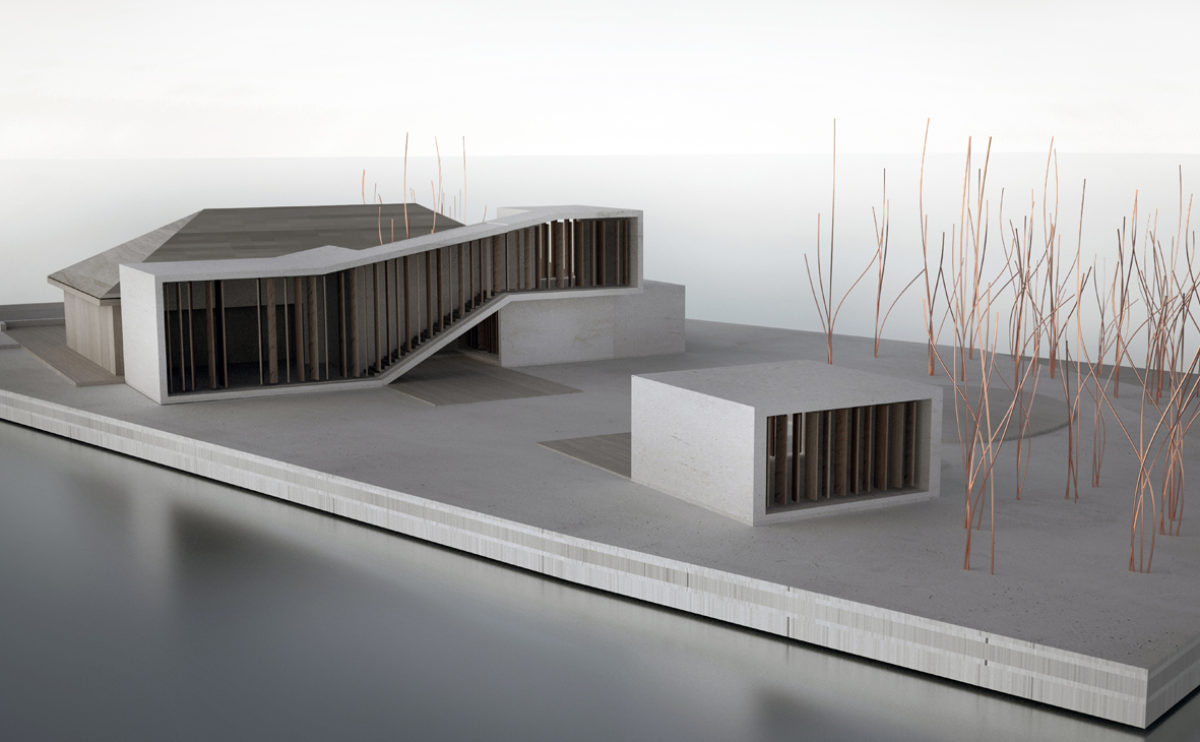
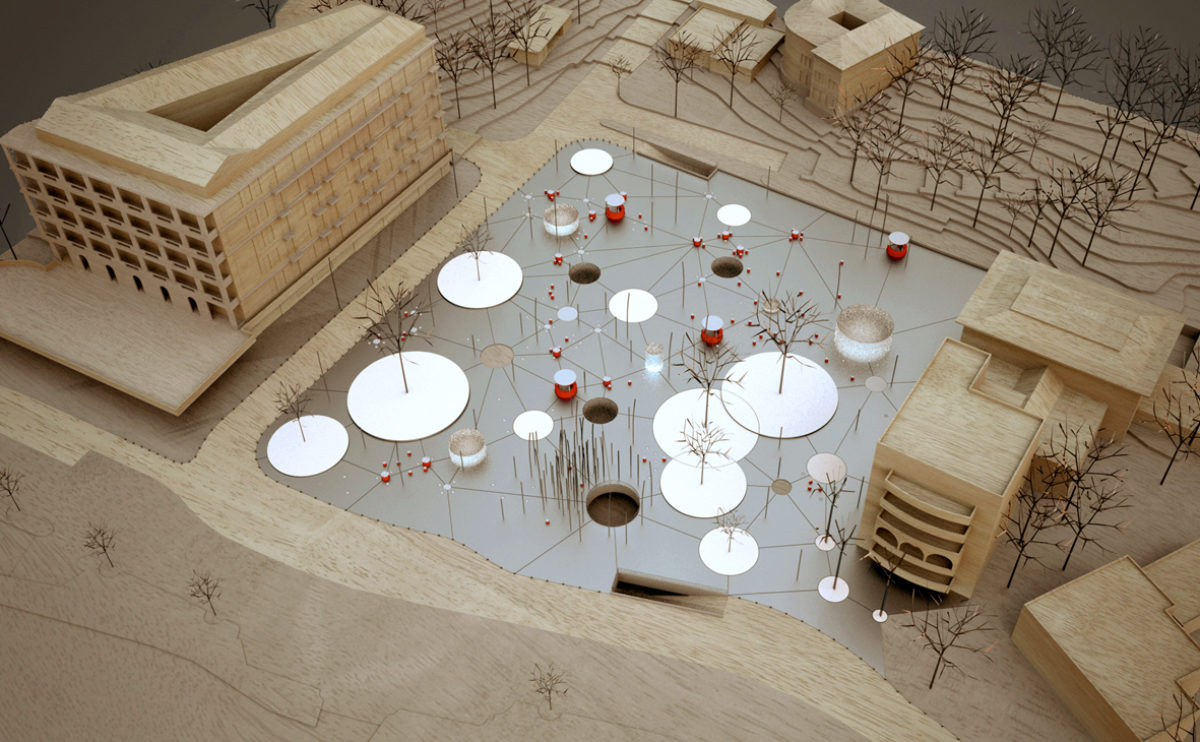
A physical model in architecture is a three-dimensional representation of a building or structure, typically constructed at a reduced scale. Physical models are often used in the design and development of buildings, and they can be an important tool for understanding and analyzing the form, layout, and spatial qualities of a design.
Physical models can be created using a variety of materials, including wood, plastic, metal, or foam, and they can be constructed using a variety of techniques, such as carving, cutting, casting, or 3D printing. Physical models can be used to represent a variety of architectural elements, including the overall form of a building, the layout of its spaces, and the materials and finishes used in its construction.
Physical models are often used as a means of visualizing and communicating design ideas, and they can be used to explore the spatial, functional, and aesthetic aspects of a design. They can also be used to test and refine design concepts, and to evaluate the performance of a design in terms of its form, layout, and spatial qualities.